Inverse Variation is nothing but if one increases the other decreases. Practice the questions in the Worksheet on Inverse Variation using Method of Proportion and learn the concept. All the Problems explained in the Worksheet help you solve inverse variation using the method of proportion. Download the easily accessible Unitary Method Inverse Variation Practice Worksheet PDF and solve the different kinds of questions framed on the topic regularly and attempt the exams with confidence.
Do Check:
- Worksheet on Direct Variation using Unitary Method
- Worksheet on Inverse Variation Using Unitary Method
Unitary Method Inverse Variation Questions
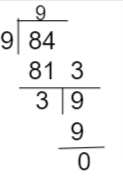
I. If 5 men can repair a road in 8 days. In how many days 10 men will repair the road?
Solution:
Given that,
5 men can repair a road in 8 days.
Here time and men are inversely proportional.
t=k/m ->eq1
Substitute m=5,t=8
8=k/5
k=40
By eq1,t=40/m
We have to find out how many days it will take for 10 men.
t=40/10=4
Hence, it will take 4 days to repair the road.
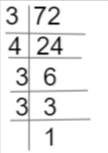
II. 5 workers can make 60 toys in 4 days. How many workers will be needed to make 216 toys in 6 days?
Solution:
Given that,
5 workers can make 60 toys in 4 days.
In one day 5 workers would make 60/4=15 toys
No. of toys are made by 1 worker in one day=15/5=3 toys.
1 day-> 3 toys
6 days->6*3=18
No. of workers needed to make 216 toys in 6 days is
216/18=12 workers
Therefore, 12 workers are required to make 108 toys.
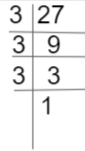
III. If 12 cows can graze a field in 10 days. Then how many cows will graze the same field in 6 days.
Solution:
Given that,
12 cows can graze a field in 10 days.
Here cows and days are inversely proportional.
t=k/m->eq1
10=k/12
k=120
subs k in eq1
t=120/m
We have to find out no. of cows required to graze the field.
6=120/m
6m=120
m=120/6=20
Therefore, 20 cows were required to graze the field in 15 days.
IV. A Bus takes 4 hours to complete a journey if it travels at a speed of 100 km/hr. How long will it take when the Bus travels at a speed of 80 km/hr?
Solution:
Given that,
A Bus takes 4 hours to complete a journey if it moves at a speed of 100 km/hr.
we know that Distance=speed × time
100 × 4= 80 × T
400=80T
T=400/80=5
Therefore, the bus takes 5 hours to complete the journey.
V. A train moves at a speed of 100 km/hr and covers a certain distance in 8.5 hours. What should be the speed of the train to cover the same distance in 5 hours?
Solution:
Given that,
Speed of the train = 100km/hr
Time = 8.5 hours
We know that Distance=speed × time
Distance = 100 × 8.5
= 850 km
Distance = 850 km
Time = 5 hours
Speed = Distance/Time
= 850/5
= 170 km/hr
Therefore, the speed of the train is 170km/hr to cover the same distance in 5 hours.
VI. In a software company, 5 employees are required to fix the bug in 9 days. Then how many employees are required to fix the bug in 5 days?
Solution:
Given that,
5 employees are required to fix the bug in 9 days.
Here employees and days are inversely proportional.
t=k/m->eq1
9=k/5
k=45
subs k in eq1
t=45/m
We have to find out no. of employees required to fix the bug.
5=45/m
5m=45
m=45/5=9
Therefore, 9 employees were required to fix the bug.
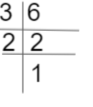
VII. If 2 men can survey the population in a town in 6 days. In how many days 6 men will do it?
Solution:
Given that,
2 men can survey the population in a town in 6 days.
Here time and men are inversely proportional.
t=k/m ->eq1
Substitute m=2,t=6
6=k/2
k=12
By eq1,t=12/m
We have to find out how many days it will take for 6 men.
t=12/6=2
Hence, it will take 2 days to repair the road.
VIII. 4 workers can stitch 48 shirts in 4 days. How many workers will be needed to make 30 shirts in 2 days?
Solution:
Given that,
4 workers can stitch 48 shirts in 4 days.
In one day 4 workers would make 48/4=12 shirts
No. of shirts are made by 1 worker in one day=12/4=3 shirts.
1 day-> 3 shirts
2 days->2*3=6
No. of workers needed to make 30 shirts in 2 days is
30/6=5 workers
Therefore, 5 workers are required to make 108 toys.