In Maths, the Area plays an important role. All the students of 9th grade can get access to the topics of Area from this page. With the help of this chapter, you can prepare thoroughly for the exams. Download the solutions of Area of all the shapes in depth. Just click on the available links to practice the problems. Find the areas of parallelograms and triangles from here. All the questions are prepared by the math experts by following the textbooks.
List of Area Concepts
Before you start preparing for the exams we suggest you guys go through the topics covered in this chapter.
- Area of a Closed Figure
- Base and Height (Altitude) in a Triangle and a Parallelogram
- Every Diagonal of a Parallelogram Divides it into Two Triangles of Equal Area
- Parallelogram on the Same Base and Between the Same Parallel Lines are Equal in Area
- Area of a Parallelogram is Equal to that of a Rectangle Between the Same Parallel Lines
- Area of a Triangle is Half that of a Parallelogram on the Same Base and between the Same Parallels
- Triangles on the Same Base and between the Same Parallels are Equal in Area
- Triangles with Equal Areas on the Same Base have Equal Corresponding Altitudes
- Problems on Finding Area of Triangle and Parallelogram
- Area of the Triangle formed by Joining the Middle Points of the Sides of a Triangle is Equal to One-fourth Area of the given Triangle
- The Area of a Rhombus is Equal to Half the Product of its Diagonals
- If Each Diagonal of a Quadrilateral Divides it in Two Triangles of Equal Area then Prove that the Quadrilateral is a Parallelogram
Area – Definition | What is Definition of Area in Math?
The area is nothing but the amount of place occupied by the two-dimensional shape or figure. In other words, we can say that area is an empty surface. There are different units to measure the area of surface likewise meters, centimeters, feet, yards, inches, and so on. The units of the area are square units.
Do Check:
How do you find Areas of Different Planar Shapes?
The area of any figure can be calculated by multiplying the dimensions of the surface. In this section, we will learn how to calculate the area of different shapes like rectangles, squares, circles, triangles, parallelogram, Rhombus, trapezium.
Area of Rectangle:
The area of a rectangle is the space occupied by the given figure. A rectangle has two dimensions length and width. The formula to calculate the area of a rectangle is the multiple of length and width.
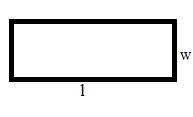
A = L × W
where,
A = Area
L = Length
W = Width
Area of Square:
The area of the square is the surface occupied by it. In a square all the sides are equal. And the sides of the square are denoted by ‘s’.
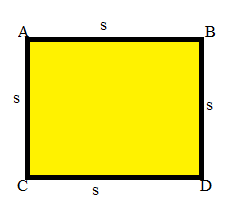
Area = s × s
where,
A = Area
s = sides of the square
Area of Circle:
The area of a circle is nothing but the measure of space covered within the boundary of the circle. The unit of area of the circle is square units.
A = Πr²
where,
A = Area of a circle
Π = pi, the value of Π is 3.14 or 22/7
r = radius of the circle
Area of Triangle:
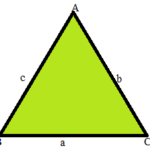
A triangle is a regular polygon with three sides and three vertices. The area of a triangle can be measured by calculating the surface of the figure.
A = 1/2 × b × h sq. units
where,
A = Area of triangle
b = base
h = height
Area of Parallelogram:
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with four sides, four vertices, and four angles. The opposite sides of the parallelogram are equal and parallel. The Area of the parallelogram can be calculated by multiplying the base and height of the given planar figure.
A = b × h sq. units
where,
A = Area of parallelogram
b = base
h = height
Area of Rhombus:
Rhombus is similar to the square where all the sides are equal. It is the shape of a diamond. It has two diagonals d1 and d2. The area of a rhombus formula is the product of half of diagonal 1 and diagonal 2.
A = 1/2 × d1 × d2 sq. units
where,
A = Area of rhombus
d1 = first diagonal
d2 = second diagonal
Area of Trapezium:
The trapezium is one of the quadrilaterals with four sides, vertices, and angles. The area of trapezium is the amount of space occupied by the geometric figure.
A = 1/2 (a + b) × h
where,
A = Area of trapezium
a and b are the sides
h is the height of the trapezium
Important Points to Remember:
1. Students have to understand that the area of space is occupied by the planar shape.
2. Area of the rectangle is length × breadth.
3. Area of the triangle is 1/2 × base × height.
4. Area of a parallelogram is base × height.
5. Congruent regions have similar areas.
Example Problems on Area
Example 1.
Find the area of a triangle with a base of 10 inches and a height of 10 inches.
Solution:
Given that
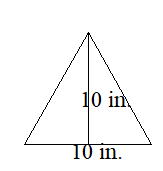
Base = 10 inches
Height = 5 inches
Area of triangle = ½ × b × h
Area of triangle = ½ × 10 × 10
Area of triangle = 50in²
Example 2.
The angle between any two sides of a parallelogram is 90 degrees. If the length of the two parallel sides is 6cm and 8 cm respectively, then find the area.
Solution:
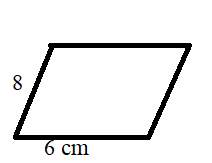
a = 6 cm and b=8 cm
x = 90 degrees
Area of Parallelogram = ab sin (x)
Area of Parallelogram = 6 × 8 sin (90)
Area of Parallelogram = 48 sin 90
Area of Parallelogram = 48 × 1 = 48 square cm.
Example 3.
Find the altitude of the rhombus whose area is 300cm² and its perimeter is 180 cm.
Solution:
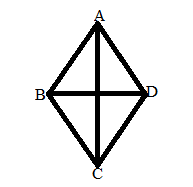
The perimeter of rhombus = 180 cm
Therefore, The side of rhombus = P/4 = 180/4 = 45 cm
Area of rhombus = base × height
300 = 45 × h
h = 300/45
h = 6.6 cm
Therefore, the altitude of the rhombus is 6.6 cm
Example 4.
Find the circumference and the area of a circle whose radius is 21 cm.
Solution:
Given that
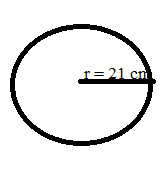
Radius of the circle = 14 cm
Circumference of the Circle = 2πr
= 2 × 22/7 × 21
= 2 × 22 × 3
= 132 cm
Area of Circle formula = πr²
= 22/7 × 21 × 21
= 22 × 3 × 21
= 1386 square cm.
Area of the Circle = 1386 square cm.
Example 5.
Two parallel sides of a trapezium are of lengths 26 cm and 18 cm respectively, and the distance between them is 14 cm. Find the area of the trapezium.
Solution:
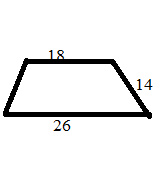
Area of the trapezium = ¹/₂ × (sum of parallel sides) × (distance between them)
= (¹/₂ × (26 + 18) × 14) cm² = 308 cm²
FAQs on Area
1. Where can I find areas of parallelograms and triangles class questions with answers?
All the students of grade 9 can get the areas of parallelograms and triangles class questions with step by step explanations @eurekamathanswers.com
2. How do you find the area?
The area is calculated by multiplying the length of a shape by its width.
3. What is the area of a figure?
The area is the amount of space occupied by a two-dimensional figure. The standard unit of area is square units.