Every object in the world around us has a shape. Those shapes are described by maths geometry. School going 9th-grade math students can learn about the concept of geometry and measurement details. From this page, you can get the complete details about triangles, their types, angles, theorems, properties and many more.
What is Geometry and Measurement?
Geometry is a branch of mathematics that studies the shapes, sizes, positions and dimensions of various objects. The word geometry is derived from two Ancient Greek words Geo means Earth, metron means measurement. Geometric and spatial thinking is important as they connect the physical world, mathematics to develop and support arithmetic and number concepts and skills.
The different types of shapes in geometry is useful to understand the shapes in our day to day life. The 2 dimension geometry shapes are triangles, squares, rectangles, circles and other flat shapes. 3D shapes are cube, cuboid, cone, square pyramid, and so on. The basics of geometry depend on the angles, points, lines and planes.
Some of the important topics of geometry are discussed through the following links.
- Triangles
- Classification of Triangles on the Basis of Their Sides and Angles
- Medians and Altitudes of a Triangle
- Geometrical Property of Altitudes
- Properties of Angles of a Triangle
- Congruency of Triangles
- Criteria for Congruency
- Problems on Congruency of Triangles
- Any point on the bisector of an angle
- An Altitude of an Equilateral Triangle is also a Median
- Bisectors of the Angles of a Triangle Meet at a Point
- Application of Congruency of Triangles
- Angles Opposite to Equal Sides of an Isosceles Triangle are Equal
- Equal Sides of an Isosceles Triangle
- The Three Angles of an Equilateral Triangle are Equal
- Sides Opposite to the Equal Angles of a Triangle are Equal
- Problems on Properties of Isosceles Triangles
- Problem on Two Isosceles Triangles on the Same Base
- Lines Joining the Extremities of the Base of an Isosceles Triangle
- Base of an Isosceles Triangle
- Theorem on Isosceles Triangle
The various branches of geometry are along the lines:
- Algebraic Geometry: It studies zeros the multivariate polynomial. Applications are cryptography, string theory and others.
- Discrete Geometry: It deals with simple geometric objects.
- Differential Geometry: It uses algebra and calculus for problem-solving.
- Euclidean Geometry: It is the study of solid figures, planes and theorems. Applications in crystallography, computer science, etc.
- Convex Geometry: It uses convex shapes in Euclidean space using techniques of real analysis.
- Topology: It is concerned with the space properties under continuous mapping.
What are Triangles & Types?
In geometry, a triangle is a type of polygon that is having three sides, three vertices and three angles. The important property of a triangle is the sum of the interior angles in it is always equal to 180 degrees. The point of intersection of two sides is called vertex and an angle is formed between two lines.
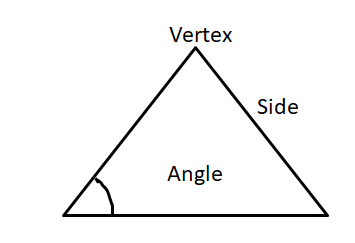
The different types of triangles based on the sides and angles are given here.
- Equilateral Triangle: If all three sides, angles are equal, then it is an equilateral triangle.
- Isosceles Triangle: If any two sides are equal, then it is an isosceles triangle.
- Scalene Triangle: If all three sides measure different, then it is a scalene triangle.
- Acute-angled Triangle: It has all three angles are less than 90°.
- Obtuse-angled Triangle: It has one or more angles greater than 90°.
- Right-angled Triangle: Anyone angle in the triangle is right angle or 90°.
Properties of Triangles
If a geometric shape is called a triangle means it should follow all these properties without fail.
- A triangle must and should have three sides, three angles.
- The sum of the interior angles in a triangle is always 180 degrees.
- The total of exterior angles of a triangle is 360 degrees.
- The sum of the consecutive interior, the exterior angles is supplementary.
- The shortest side of a triangle is always opposite to the smallest interior angle. Likewise, the longest side is opposite to the largest interior angle.
- The difference between the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is less than the length of the third side. Similarly, the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of the third side.
Congruency of Triangles
Congruence is a term used to define an object and its mirror image. Two triangles are said to be congruent when all three corresponding sides, angles are equal in measure. There are four congruency rules that prove two triangles are congruent. Conditions for Congruence of Triangles are mentioned here:
- SSS (Side-Side-Side)
- SAS (Side-Angle-Side)
- ASA (Angle-Side-Angle)
- AAS (Angle-Angle-Side)
- RHS (Right angle-Hypotenuese-Side)
Solved Examples
Example 1:
In ∆XYZ, ∠X = 80°, ∠Y = 50°. Find ∠Z.
Solution:
Given that,
∠X = 80°, ∠Y = 50°
In a triangle, the sum of interior angles is 180 degrees.
So, ∠X + ∠Y + ∠Z = 180°
80° + 50° + ∠Z = 180°
130° + ∠Z = 180°
∠Z = 180°- 130°
∠Z = 50°
Example 2:
If ∆ABC is a right angled triangle, ∠B = 40°. Find other two angles.
Solution:
Given that,
∆ABC is a right-angled triangle. So, any one angle is 90°.
∠B = 40°
In a triangle, the sum of interior angles is 180 degrees.
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
90° + 40° + ∠C = 180°
∠C = 180° – 130°
∠C = 50°
FAQ’s on Geometry & Measurement
1. What are the geometry applications?
Geometry is used in daily life. It has a wide range of applications in the field of construction, surveying, mapping, software industries and many more.
2. What are the different shapes in geometry?
The different shapes of geometry are lines, points, triangles, rectangles, squares, quadrilaterals, cone, cube, cuboid, square pyramid, pentagon pyramid and so on.
3. What are the angles in geometry?
In planar geometry, the angle is formed by joining two rays. The common end point of those rays is called the vertex of the angle. The four types of angles are obtuse angle, acute angle, right angle and straight angle.