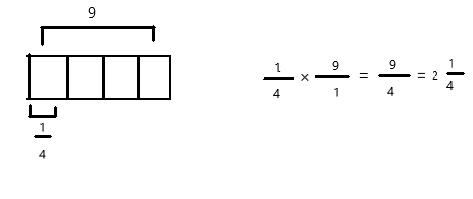Engage NY Eureka Math 5th Grade Module 4 Lesson 17 Answer Key
Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 4 Lesson 17 Problem Set Answer Key
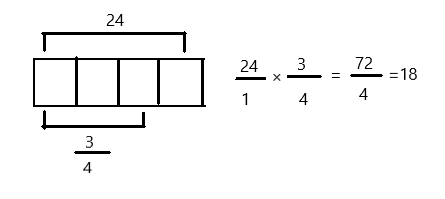
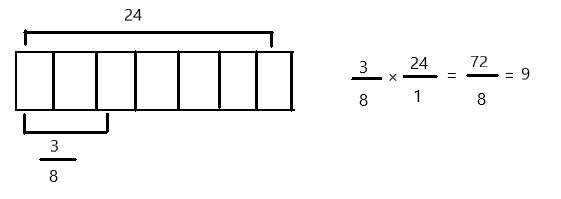
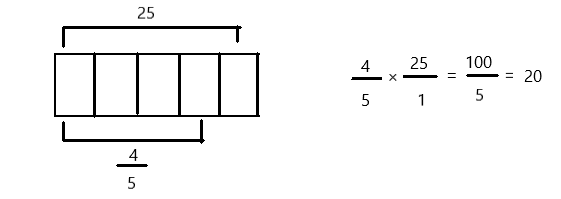
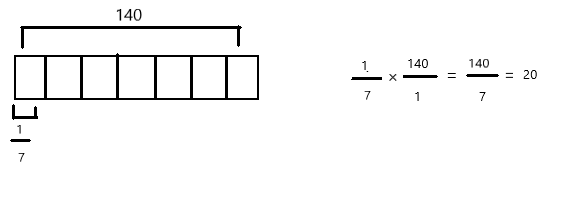
Question 1.
Multiply and model. Rewrite each expression as a multiplication sentence with decimal factors. The first one is done for you.
\(\frac{1}{10}\) × \(\frac{1}{10}\)
= \(\frac{1 × 1}{10 × 10}\)
= \(\frac{1}{100}\)
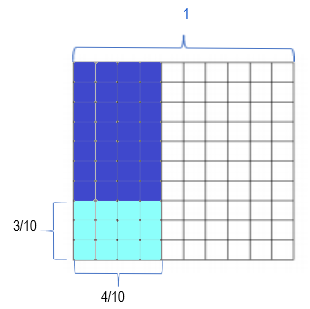
b. \(\frac{4}{10}\) × \(\frac{3}{10}\)
Answer:
Explanation:
Given that \(\frac{4}{10}\) × \(\frac{3}{10}\)
= \(\frac{4 × 3}{10 × 10}\)
= \(\frac{12}{100}\)
= 0.12.
c. \(\frac{1}{10}\) × 1.4
d. \(\frac{6}{10}\) × 1.7
Question 2.
Multiply. The first few are started for you.
a. 5 × 0.7 = _______
= 5 × \(\frac{7}{10}\)
= \(\frac{5 × 7}{10}\)
= \(\frac{35}{10}\)
= 3.5
b. 0.5 × 0.7 = ___
= \(\frac{5}{10}\) × \(\frac{7}{10}\)
= \(\frac{5 × 7}{10 × 10}\)
= \(\frac{35}{100}\)
= 0.35
c. 0.05 × 0.7 = __
= \(\frac{5}{100}\) × \(\frac{7}{10}\)
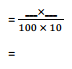
= \(\frac{5}{7}\) × \(\frac{10}{100}\)
= \(\frac{35}{1000}\)
= 0.035
d. 6 × 0.3 = _______
= 6 × \(\frac{3}{10}\)
= \(\frac{6 × 3}{10}\)
= \(\frac{18}{10}\)
= 1.8
e. 0.6 × 0.3 = _______
= \(\frac{6}{10}\) × \(\frac{3}{10}\)
= \(\frac{6 × 3}{10 × 10}\)
= \(\frac{18}{100}\)
= 0.18
f. 0.06 × 0.3 = _______
= \(\frac{6}{100}\) × \(\frac{3}{10}\)
= \(\frac{6 × 3}{100 × 10}\)
= \(\frac{18}{1000}\)
= 0.018
g. 1.2 × 4 = _______
= \(\frac{12}{10}\) × 4
= \(\frac{12 × 4}{10}\)
= \(\frac{48}{10}\)
= 4.8.
h. 1.2 × 0.4 = _______
= \(\frac{12}{10}\) × \(\frac{4}{10}\)
= \(\frac{12 × 4}{10 × 10}\)
= \(\frac{48}{100}\)
= 0.48.
i. 0.12 × 0.4 = _______
= \(\frac{12}{100}\) × \(\frac{4}{10}\)
= \(\frac{12 × 4}{100 × 10}\)
= \(\frac{48}{1000}\)
= 0.048.
Question 3.
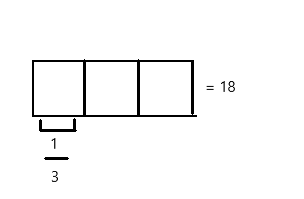
A Boy Scout has a length of rope measuring 0.7 meter. He uses 2 tenths of the rope to tie a knot at one end. How many meters of rope are in the knot?
Question 4.
After just 4 tenths of a 2.5-mile race was completed, Lenox took the lead and remained there until the end of the race.
a. How many miles did Lenox lead the race?
b. Reid, the second-place finisher, developed a cramp with 3 tenths of the race remaining. How many miles did Reid run without a cramp?
Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 4 Lesson 17 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Question 1.
Multiply and model. Rewrite the expression as a number sentence with decimal factors.
\(\frac{1}{10}\) × 1.2
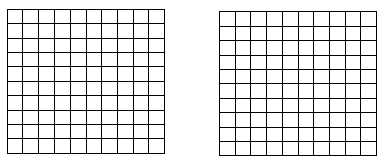
Question 2.
Multiply.
a. 1.5 × 3 = _______
b. 1.5 × 0.3 = _______
c. 0.15 × 0.3 = _______
Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 4 Lesson 17 Homework Answer Key
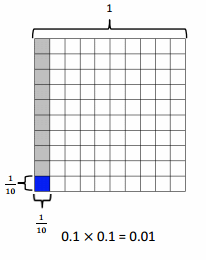
Question 1.
Multiply and model. Rewrite each expression as a number sentence with decimal factors. The first one is done for you.
a. \(\frac{1}{10}\) × \(\frac{1}{10}\)
= \(\frac{1 × 1}{10 × 10}\)
= \(\frac{1}{100}\)
0.1 × 0.1 = 0.01
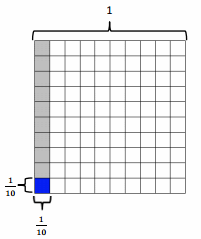
b. \(\frac{6}{10}\) × \(\frac{2}{10}\)
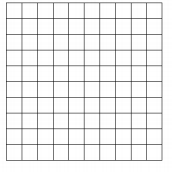
c. \(\frac{1}{10}\) × 1.6
d. \(\frac{6}{10}\) × 1.9
Question 2.
Multiply. The first few are started for you.
a. 4 × 0.6 = _______
= 4 × \(\frac{6}{10}\)
= \(\frac{4 × 6}{10}\)
= \(\frac{24}{10}\)
= 2.4
b. 0.4 × 0.6 = _______
= \(\frac{4}{10}\) × \(\frac{6}{10}\)
= \(\frac{4 × 6}{10 × 10}\)
=
c. 0.04 × 0.6 = _______
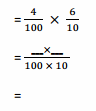
d. 7 × 0.3 = _______
e. 0.7 × 0.3 = _______
f. 0.07 × 0.3 = _______
g. 1.3 × 5 = _______
h. 1.3 × 0.5 = _______
i. 0.13 × 0.5 = _______
Question 3.
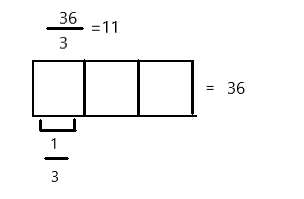
Jennifer makes 1.7 liters of lemonade. If she pours 3 tenths of the lemonade in the glass, how many liters of lemonade are in the glass?
Question 4.
Cassius walked 6 tenths of a 3.6-mile trail.
a. How many miles did Cassius have left to hike?
b. Cameron was 1.3 miles ahead of Cassius. How many miles did Cameron hike already?