Trigonometry Ratios Table 0-360: Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the study of the length and angles of a triangle. It is usually associated with a right-angle triangle in which one of the angles is 90 degrees. It has a vast number of applications in the field of mathematics. You can figure out many geometrical calculations much simpler if you are aware of the Trigonometric Functions and Table.
Trigonometric Ratios Table help you find the trigonometric standard angles such as 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90°. You can find Trigonometric Ratios such as sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, cotangent, etc. In short, you can write the Trigonometric Ratios as sin, cos, tan, cosec, sec, and cot. You can solve Trigonometry Problems easily if you know the standard values of the Trigonometric Ratios. Thus, remember the standard angle values to make your job easier.
Trigonometric Table has a wide range of applications and it was used ever since before the existence of calculators. Another Important Application of the Trigonometric Table is in the Fast Fourier Transforms.
Trigonometric Ratios Table for Standard Angles
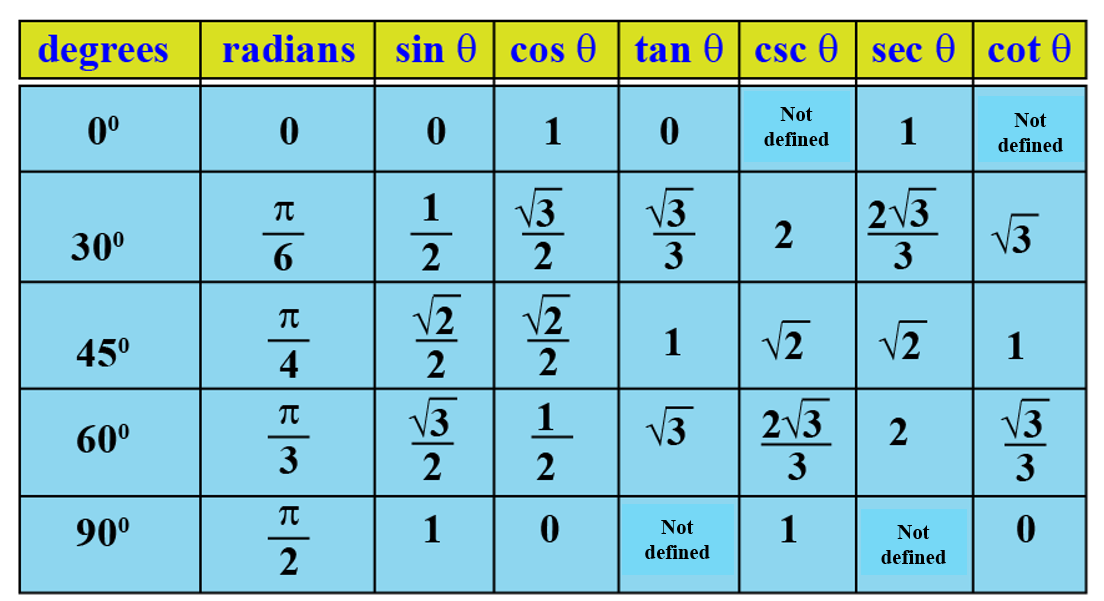
Trig Values Table: 0 to 360 Degrees
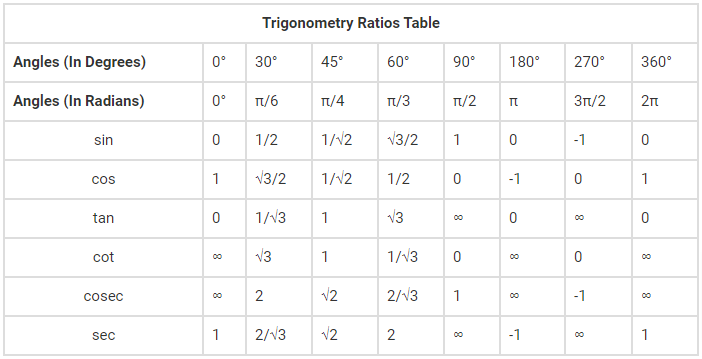
Tricks to Remember Trigonometry Table
It is easy to remember the trigonometry table. If you are aware of the trigonometric formulas remembering the table is quite simple. The Trigonometric Ratios Table is dependant on the Trigonometric Formulas. Try to remember the trigonometric table easily by going through the simple formulas.
- sin x = cos (90° – x)
- cos x = sin (90° – x)
- tan x = cot (90° – x)
- cot x = tan (90° – x)
- sec x = cosec (90° – x)
- cosec x = sec (90° – x)
- 1/sin x = cosec x
- 1/cos x = sec x
- 1/tan x = cot x
How to Create a Trigonometric Ratio Table?
Check out the simple guidelines listed below to create a Trigonometric Table having Values of Standard Angles. They are in the following fashion
Step 1:
Create a table having the top row and list out the angles 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 90° and also write trigonometric functions such as sin, cos, tan, cosec, sec, cot.
Step 2: Determine the Value of Sin
In the second step determine the value of sin, divide 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 by 4 under the root.
\(\sqrt{\frac{0}{4}}=0\)
| Angles (In Degrees) | 0° | 30° | 45° | 60° | 90° | 180° | 270° | 360° |
| sin | 0 | 1/2 | 1/√2 | √3/2 | 1 | 0 | -1 | 0 |
Step 3: Determine the Value of Cos
Cos is opposite to sin and to find the value of cos divide by 4 in the opposite sequence of sin. For instance, divide 4 with 4 under the root to obtain the value of cos 0°
\(\sqrt{\frac{4}{4}}=1\)
| Angles (In Degrees) | 0° | 30° | 45° | 60° | 90° | 180° | 270° | 360° |
| cos | 1 | √3/2 | 1/√2 | 1/2 | 0 | -1 | 0 | 1 |
Step 4: Determine the value of tan
Tan is obtained by dividing sin with cos. To find the value of tan 0° divide the Value of Sin 0° by the Value of Cos 0°.
| Angles (In Degrees) | 0° | 30° | 45° | 60° | 90° | 180° | 270° | 360° |
| tan | 0 | 1/√3 | 1 | √3 | ∞ | 0 | ∞ | 0 |
Step 5: Determine the value of the cot
Value of cot is equal to reciprocal of tan. The value of cot at 0° is obtained by dividing 1 with the value of tan at 0°. In the same way, you can find the value of the cot for all the angles.
| Angles (In Degrees) | 0° | 30° | 45° | 60° | 90° | 180° | 270° | 360° |
| cot | ∞ | √3 | 1 | 1/√3 | 0 | ∞ | 0 | ∞ |
Step 6: Determine the value of cosec
Cosec value at 0° is the reciprocal of sin at 0°. You can find all the angles of cosec as such
| Angles (In Degrees) | 0° | 30° | 45° | 60° | 90° | 180° | 270° | 360° |
| cosec | ∞ | 2 | √2 | 2/√3 | 1 | ∞ | -1 | ∞ |
Step 7: Determine the value of sec
sec values can be obtained by the reciprocal values of cos. Sec value at 0° is the opposite of cos on 0°. In the similar way entire table of values is given.
| Angles (In Degrees) | 0° | 30° | 45° | 60° | 90° | 180° | 270° | 360° |
| sec | 1 | 2/√3 | √2 | 2 | ∞ | -1 | ∞ | 1 |
FAQs on Trigonometric Ratios Table
1. How to find the Trigonometric Functions Values?
All the Trigonometric Functions Values can be found easily using the formulas and they are given as such
- Sin = Opposite/Hypotenuse
- Cos = Adjacent/Hypotenuse
- Tan = Opposite/Adjacent
- Cot = 1/Tan = Adjacent/Opposite
- Cosec = 1/Sin = Hypotenuse/Opposite
- Sec = 1/Cos = Hypotenuse/Adjacent
2. What is Trigonometric Values Table?
Trigonometric Values table is made of trigonometric ratios that are interrelated to each other – sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, cotangent.
3. What are Trigonometric Ratios?
Trigonometric Ratios is a relationship between measurements of length and angles of a right angle triangle.