A Linear Equation is a mathematical statement including one variable in it. Usually to solve variables in a linear equation number of equations should be equal to the number of variables. It is the same with Linear Equations in one variable you need only one equation to find the variable in it. This article of ours covers everything on the solution of a linear equation definition, types of solutions of linear equations, how to solve a linear equation in one variable with examples.
What is the Solution of a Linear Equation?
Solution of a Linear Equation is nothing but the points at which the lines or planes denoting the linear equations meet. The solution set of a system of linear equations is nothing but the set of values to the variables of all possible solutions.
Types of Solutions of Linear Equations
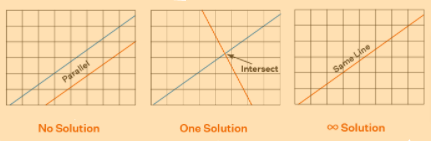
A System of Linear Equations has 3 types of solutions. We have listed all of them with enough explanatory diagrams for your reference.
Unique Solution of System of Linear Equations
Unique Solution of System of Linear Equations tells us that there is only one point and on substituting which L.H.S is equal to R.H.S. In the Case of Simultaneous Linear Equations in Two Variables unique solution is an ordered pair(x,y) that satisfies both equations.
No Solution
The System of Linear Equations has no solution when the lines don’t intersect or meet at any point, graphs of linear equations are parallel.
Infinite Solutions
A System of Linear Equations has infinite solutions if there exist infinite solutions for a solution set for which L.H.S and R.H.S become equal, or the graph includes straight lines overlapping each other.
How to Solve a Linear Equation in One Variable?
Follow the step-by-step process listed below for solving a linear equation in one variable. They are along the lines
- Go through the given linear equation carefully.
- Figure out the quantity you need to find out.
- Simply split the equation into two parts as L.H.S and R.H.S
- Identify the terms having constants and variables.
- Transfer all the constants to R.H.S of Equation and Variables to L.H.S of the equation.
- Perform Algebraic Operations on both sides to determine the value of the variable.
Linear Equations in One Variable Questions
Example 1.
Solve x +15 = 32?
Solution:
Given x +15 = 32
Let us transfer the constants and variables on the R.H.S and L.H.S
x=32-15
=17
Example 2.
Solve 3x+60=6x-30?
Solution:
Given 3x+60=6x-30
Transfering the constants and variables to their respective sides we can write 60+30=6x-3x
90=3x
x=90/3
x=30
Example 3.
The sum of the two numbers is 48. If one number is 5 times the other, find the numbers?
Solution:
Let the number be x
Since the other number is 5 times the other = 5x
Given Sum of 2 Numbers = 48
x+5x=48
6x=48
x=48/6 =8
Other Number =5x =5*8=40
Example 4.
Sam loves to collect ¢5 and ¢10 coins in his piggy bank. He knows that the total sum in his piggy bank is ¢90, and it has 4 times as many two-cent coins as five-cent coins in it. He wants to know the exact number of ¢5 and ¢10 coins in his piggy bank. Can you help him find the count?
Solution:
Let the number of ¢5 coins be x.
The number of ¢10 coins will be 4x.
Total amount = 5x + 10(4x)
Thus, 5x + 10(4x) = 90
5x + 40x = 90
45x = 90
x = 90/45=2
Therefore, sam has 2 coins ¢5 of and 20 coins of ¢10.