Big Ideas Math Answers Grade K Chapter 13 Identify Measure and Compare Objects: Join the list of top-ranking students by using the Big Ideas Math Answers Grade K. Get access to Download Big Ideas Math Book Grade K Answer Key Chapter 13 Measure and Compare Objects for free. We have to prepare the solutions in such a way that all the students can understand the concept easily. Quick and easy learning is possible only in our Big Ideas Math Book Grade K Solution Key Chapter 13 Measure and Compare Objects.
Big Ideas Math Book Grade K Answer Key Chapter 13 Measure and Compare Objects
We suggest the students to refer the Big Ideas Math Book Grade K Answer Key Chapter 13 Measure and Compare Objects to gain the highest score in exams. This creates interest in students to become masters in maths. Learn the concepts of Measure and Compare Objects in such a way that you prepare the questions on your own. Click on the below attached and link below and get the step by step explanation.
Vocabulary
Lesson: 1 Compare Heights
Lesson: 2 Compare Lengths
Lesson: 3 Use Number to Compare Lengths
Lesson: 4 Compare Weights
Lesson: 5 Use Numbers to Compare Weights
Lesson: 6 Compare Capacities
Lesson: 7 Describe Objects by Attributes
Chapter 13: Measure and Compare Objects
- Measure and Compare Objects Performance Task
- Measure and Compare Objects Activity
- Measure and Compare Objects Chapter Practice
- Measure and Compare Objects Cumulative Practice
Measure and Compare Objects Vocabulary
Review Words
fewer
more
Answers:
Fewer:
less amount or the small amount which is countable
more:
many or more amount which is rarely countable, In some cases uncountable
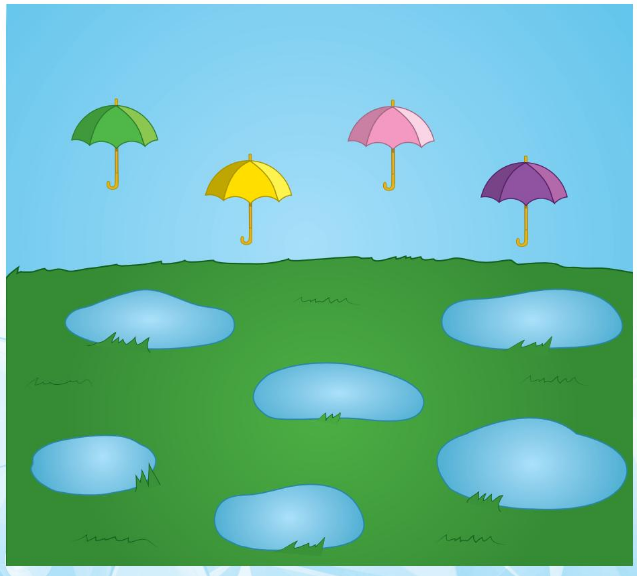
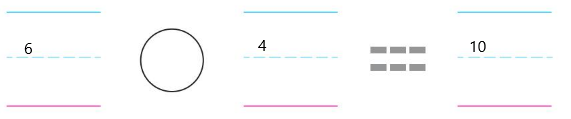
From the below diagram umbrellas are 4 which are less in amount
The water pounds are 6 when compared with umbrellas those water pounds are more

Vocabulary Cards
Lesson 13.1 Compare Heights
Explore and Grow
Directions:
Cut out the Height Sort Cards. Compare the objects to the children shown. Then sort the cards into the categories shown.
Answer:
The children shown for heights.

Explanation:
Compared the heights of the objects and cut the high sort cards and pasted them according to their heights.
Think and Grow
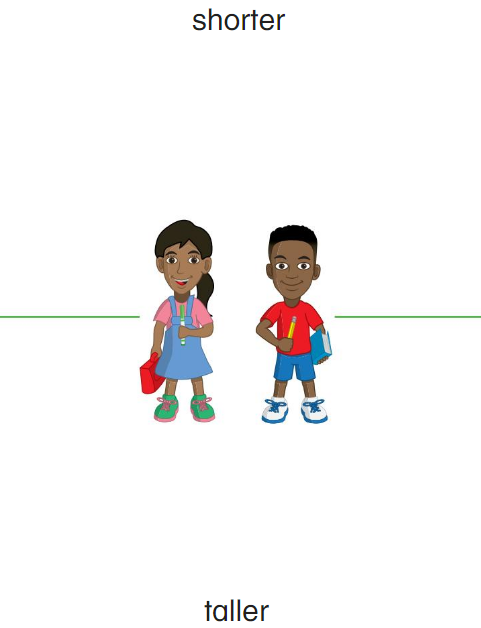
Directions: Compare the heights of the objects.
• Circle the taller slide.
• Draw a line through the shorter lamp.
Are the mugs the same height? Circle the thumbs up for yes or the thumbs down for no.

Answer: circled the taller one.
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
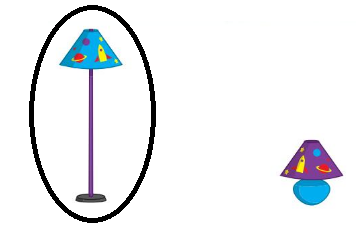
step 2: line drawn through the shorter lamp
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
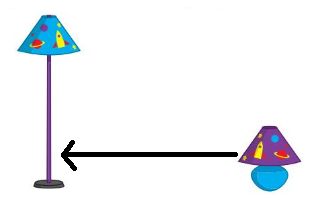
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.

Answer: Yes, the mugs are of the same height.
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.

Apply and Grow: Practice
Directions:
1 and 2 Circle the taller object. 3 and 4 Draw a line through the shorter object. 5 Are the lion and the giraffe the same height? Circle the thumbs up for yes or the thumbs down for no.
Question 1.
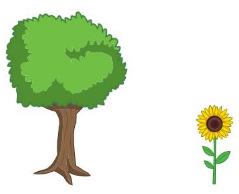
Answer: Circled the taller object
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
Question 2.

Answer: circled the taller object
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
Question 3.
Answer: line drawn through small to big
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
Question 4.

Answer: line drawn through smaller one
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
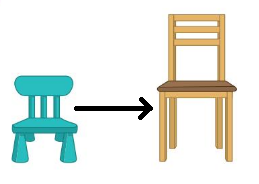
Question 5.

Answer: lion and giraffe are not same height.
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.

Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Directions:
• Draw a building that is taller than the building shown.
• Draw a building that is shorter than the building shown.
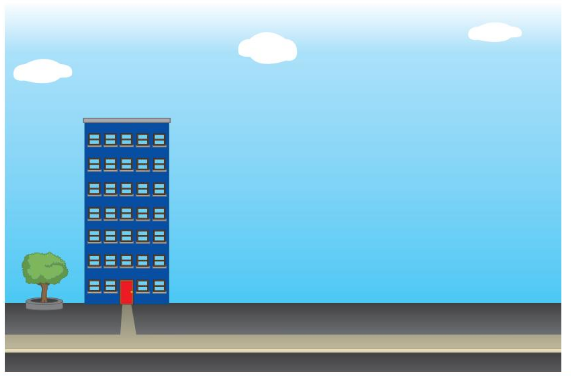
Answer:
Building drawn taller than the building shown
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.

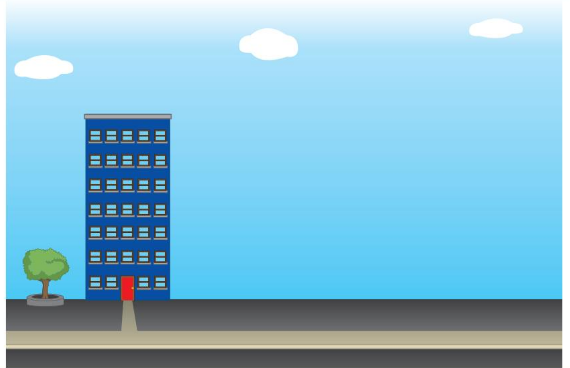
Answer:
Building drawn shorter than the building shown
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
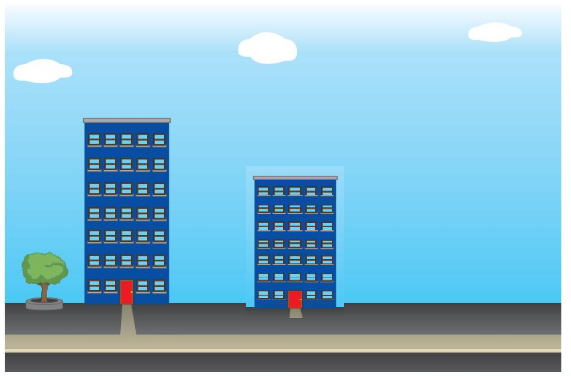
Compare Heights Homework & Practice 13.1
Directions:
1 and 2 Circle the taller object. 3 and 4 Draw a line through the shorter object.
Question 1.

Answer:
Circled the taller object
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.

Question 2.

Answer:
Circled the taller object.
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
Question 3.

Answer:
Drawn the line through the shorter object
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
Question 4.

Answer:
Drawn line through the shorter object
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
Directions:
5 and 6 Are the objects the same height? Circle the thumbs up for yes or the thumbs down for no. 7 Draw a building that is the same height as the building shown.
Question 5.

Answer:
No they are not same height.
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.

Question 6.
Answer:
The two rockets are of same height
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
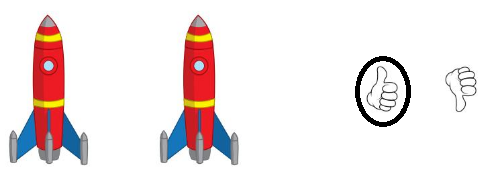
Question 7.
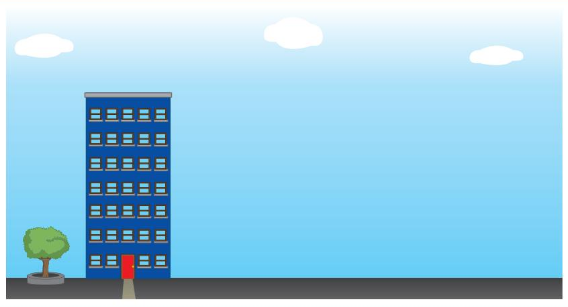
Answer:
Building drawn equal to the building shown.
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
Lesson 13.2 Compare Lengths
Explore and Grow
Directions: Cut out the Length Sort Cards. Compare the objects to the pencil shown. Then sort the cards into the categories shown.
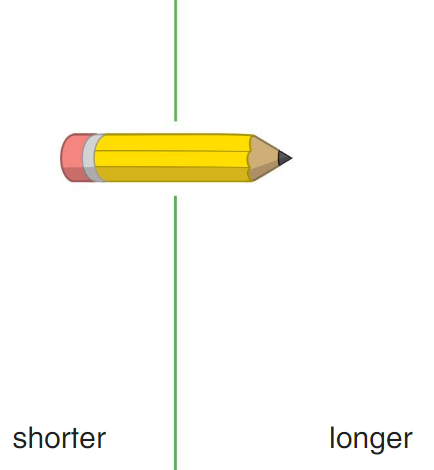
Answer:
The right giraffe is longer
the left giraffe is shorter
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
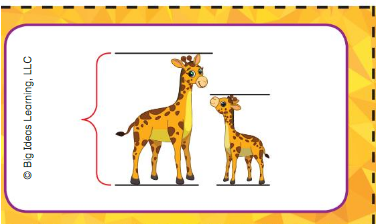
the second picture to represent height and short from the sort out pictures
first girraffe is longer than the second one
second geraffe is shorter than the first one.
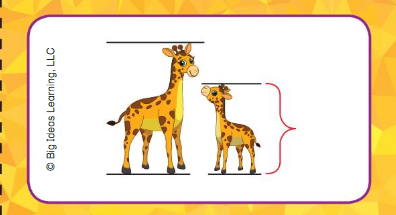
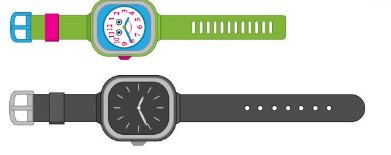
Think and Grow
Directions: Compare the lengths of the objects.
• Circle the longer surfboard.
• Draw a line through the shorter watch.
• Are the shoes the same length? Circle the thumbs up for yes or the thumbs down for no.
Answer:
Circle drawn through the longer surfboard.
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
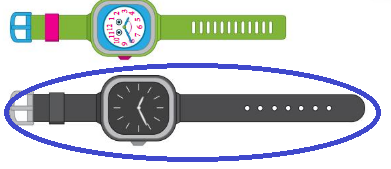
step 2:
line drawn through the shorter watch.
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
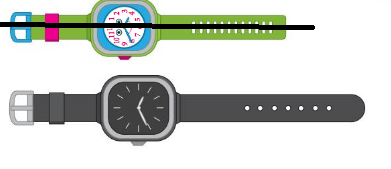

Answer:
The shoes are not in same height
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.

Apply and Grow: Practice
Directions:
1 and 2 Circle the longer object. 3 and 4 Draw a line through the shorter object
Question 1.

Answer:
Circled the longer object
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
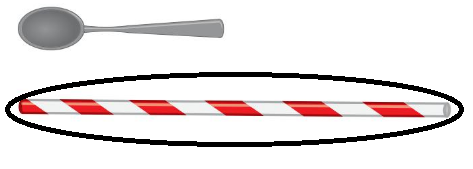
Question 2.
Answer:
Circled the longer object.
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
Question 3.
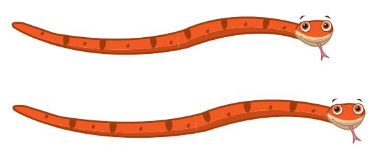
Answer:
Line drawn through the shorter object
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
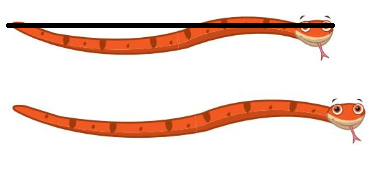
Question 4.

Answer:
Line drawn through the shorter object
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.

Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Directions:
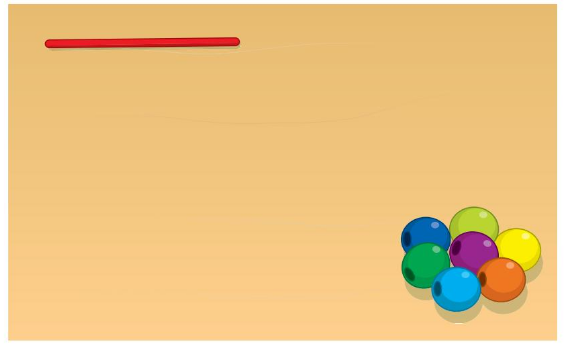
• Draw a string that holds fewer beads than the string shown. Tell how you know.
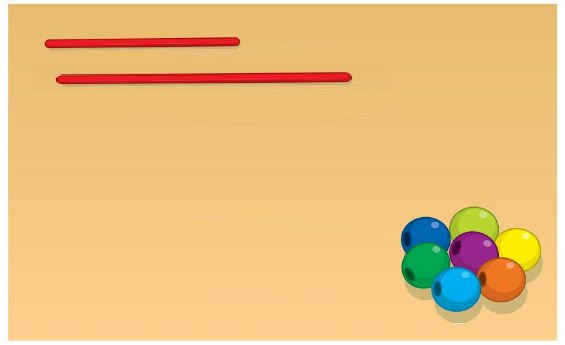
• Draw a string that holds the same number of beads as the string shown. Tell how you know.

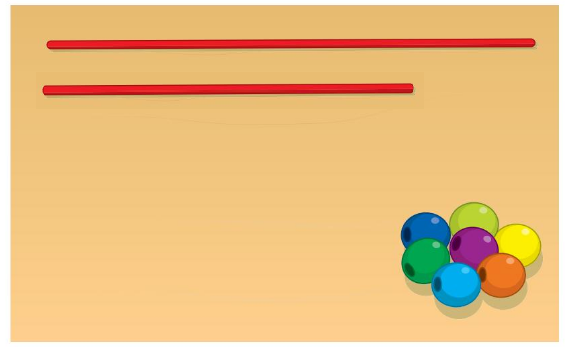
Answer:
string that holds fewer beads than the string shown
the below figure shows the small string
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.

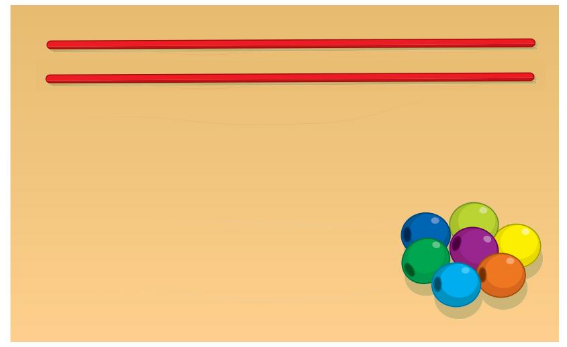
Answer:
string that holds the same number of beads as the string shown
above figure shows equal strings
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
Compare Lengths Homework & Practice 13.2
Directions:
1 and 2 Circle the longer object. 3 and 4 Draw a line through the shorter object.
Question 1.
Answer:
Circled the longer object
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
Question 2.

Answer:
Circled the longer object
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.

Question 3.

Answer:
Line drawn through the shorter object
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
Question 4.

Answer:
Line drawn through the shorter object
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
Directions:
5 and 6 Are the objects the same length? Circle the thumbs up for yes or the thumbs down for no. 7 Draw a string that holds more beads than the string shown. Tell how you know.
Question 5.

Answer:
The above object has same length
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.

Question 6.
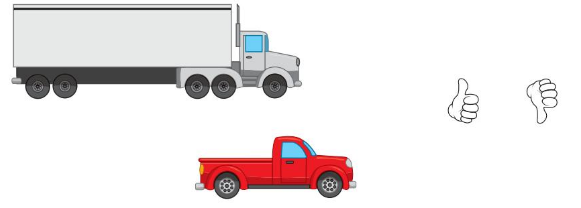
Answer:
The above objects are not equall
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
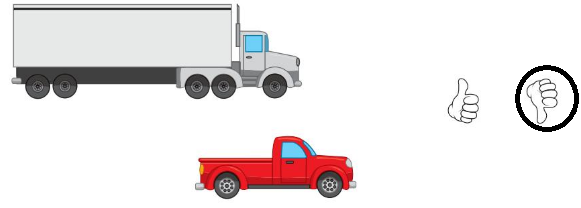
Question 7.
Answer:
The below figure shows the string that holds more beads
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
Lesson 13.3 Use Number to Compare Lengths
Explore and Grow
Directions: Build a linking cube train with 4 cubes. Circle the objects that are longer than the cube train.

Answer:
All the objects are longer.
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
the measurement or extent of something from end to end; the greater of two or the greatest of three dimensions of an object
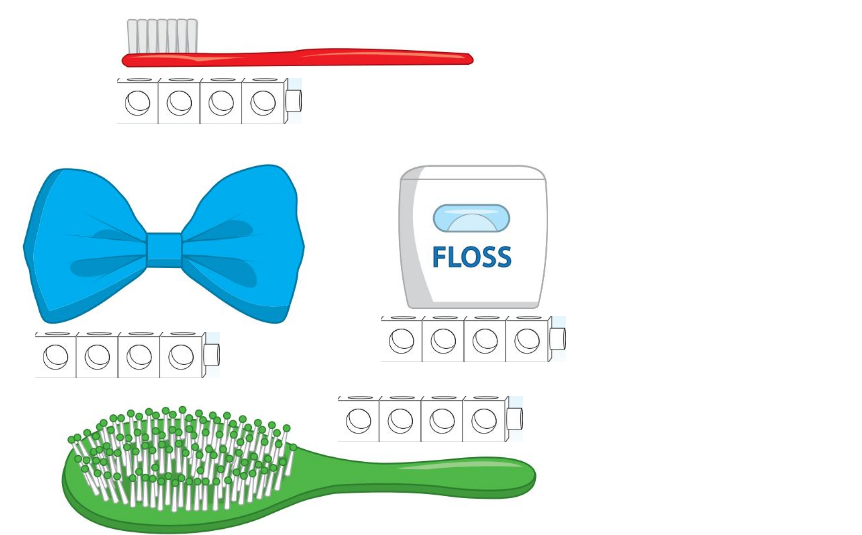
Think and Grow
Directions: Compare the lengths of the cube trains with the given number of cubes.
• Circle the number of the train that is longer. Color to show how you know.
• Draw a line through the number of the train that is shorter. Color to show how you know.
• Are the cube trains the same length? Circle the thumbs up for yes or the thumbs down for no. Color to show how you know.
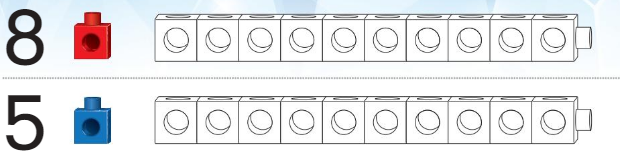
Answer:
The longer number train is circled and colored.
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
the measurement or extent of something from end to end; the greater of two or the greatest of three dimensions of an object
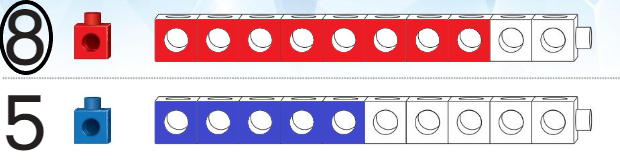
Answer:
Line drawn through the shorter train.
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
the measurement or extent of something from end to end; the greater of two or the greatest of three dimensions of an object
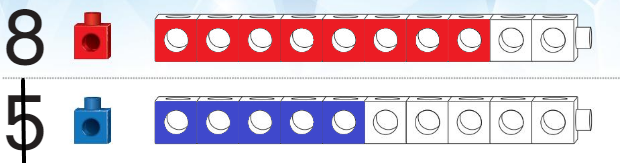
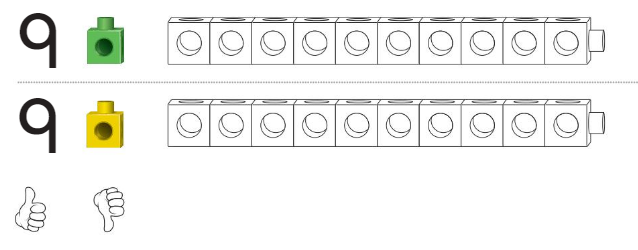
Answer:
Both the trains are equal.
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
the measurement or extent of something from end to end; the greater of two or the greatest of three dimensions of an object
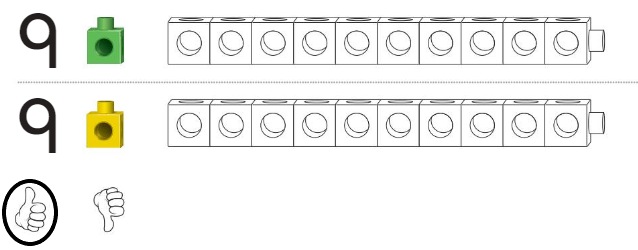
Apply and Grow: Practice
Directions:
Compare the lengths of the cube trains with the given number of cubes. 1 and 2 Circle the number of the train that is longer. Color to show how you know. 3 Draw a line through the number of the train that is shorter. Color to show how you know.
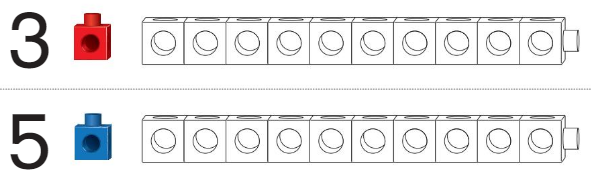
Question 1.
Answer:
Circled the number of the train that is longer
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
the measurement or extent of something from end to end; the greater of two or the greatest of three dimensions of an object
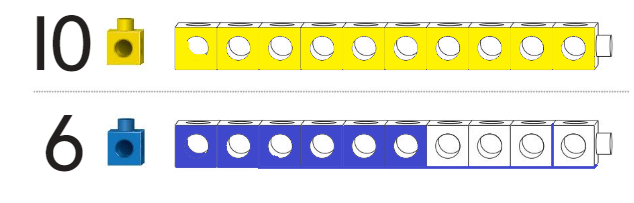
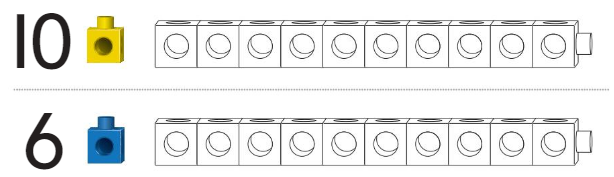
Question 2.
Answer:
Circled the train which is longer and colored
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
the measurement or extent of something from end to end; the greater of two or the greatest of three dimensions of an object
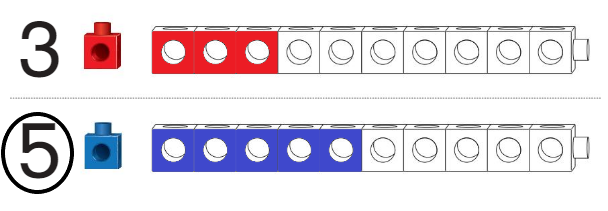
Question 3.
Answer:
Line drawn through the shorter train
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
the measurement or extent of something from end to end; the greater of two or the greatest of three dimensions of an object
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Directions: Each car on a roller coaster holds 2 people.
• Do the roller-coaster trains hold the same number of people? Circle the thumbs up for yes or the thumbs down for no. Tell how you know.
• Circle the roller-coaster train that holds more people. Tell how you know
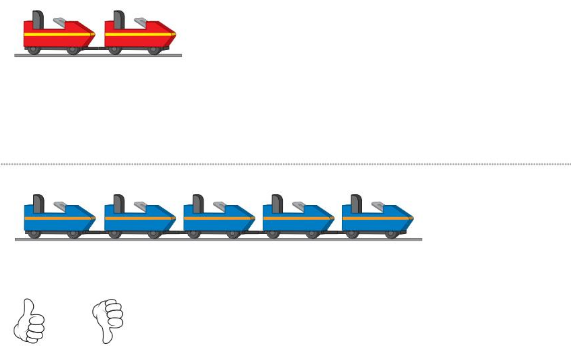
Answer:
No, The roller-coaster trains does not hold the same number of people.
the first roller -coaster contains two seats that means 4 people and the second has 5 seats with 10 people
second has more number of seats and more people
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
the measurement or extent of something from end to end; the greater of two or the greatest of three dimensions of an object
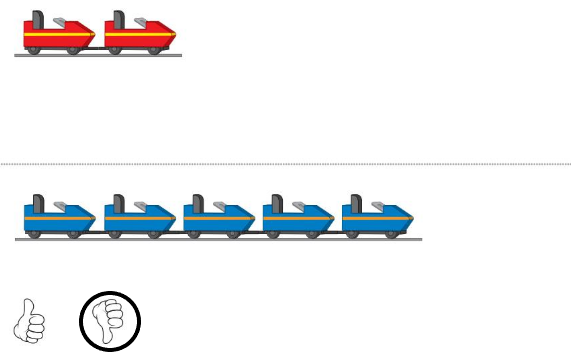
Answer: Circled the roller-coaster train that holds more people. The first roller-coaster has 4 seats with 8 people
and the second roller-coaster has 6 seats with 12 people.
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
the measurement or extent of something from end to end; the greater of two or the greatest of three dimensions of an object
Use Number to Compare Lengths Homework & Practice 13.3
Directions:
1 and 2 Compare the lengths of the cube trains with the given number of cubes. Circle the number of the train that is longer. Color to show how you know.
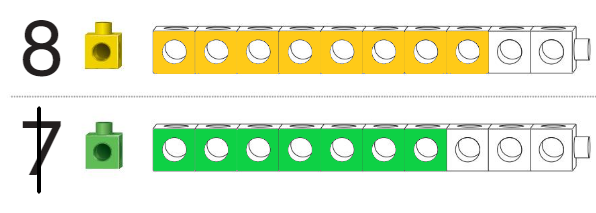
Question 1.
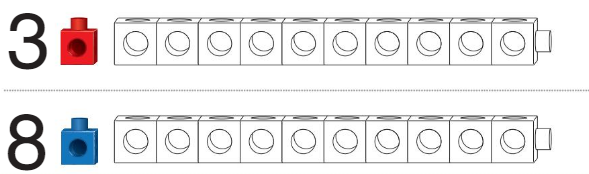
Answer:
Circled the number of the train that is longer
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
the measurement or extent of something from end to end; the greater of two or the greatest of three dimensions of an object
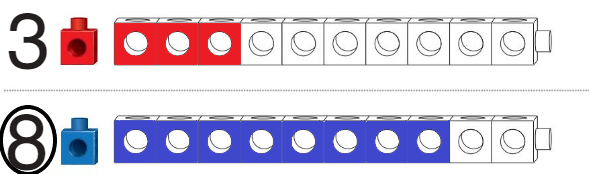
Question 2.
Answer:
Circled the longer train and colored.
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
the measurement or extent of something from end to end; the greater of two or the greatest of three dimensions of an object
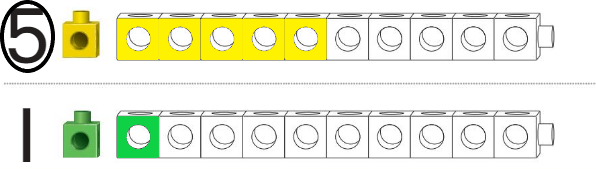
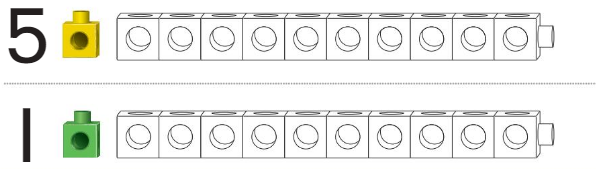
Directions:
3 Compare the lengths of the cube trains with the given number of cubes. Draw a line through the number of the train that is shorter. Color to show how you know. 4 Compare the lengths of the cube trains with the given number of cubes. Are the cube trains the same length? Circle the thumbs up for yes or the thumbs down for no. Color to show how you know. 5 Each car on a roller coaster holds 2 people. Draw a line through the roller-coaster train that holds fewer people. Tell how you know.
Question 3.
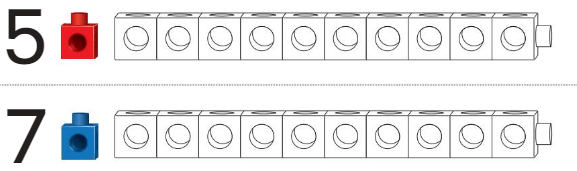
Answer:
Line through the number train that is shorter.
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
the measurement or extent of something from end to end; the greater of two or the greatest of three dimensions of an object
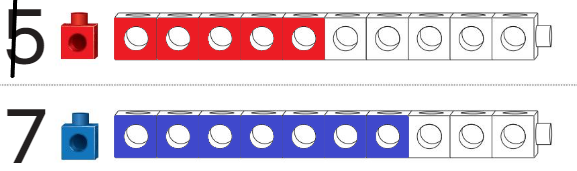
Question 4.
Answer:
No, The both trains are not equal
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
the measurement or extent of something from end to end; the greater of two or the greatest of three dimensions of an object
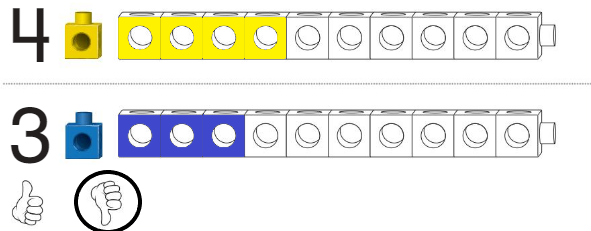
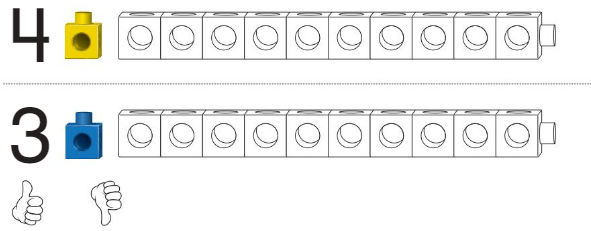
Question 5.
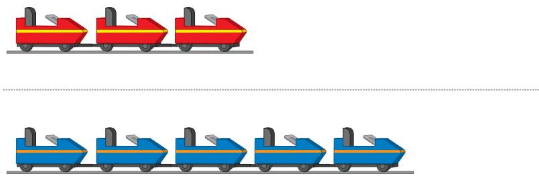
Answer:
Line drawn through the roller-coaster which contains fewer people
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
the measurement or extent of something from end to end; the greater of two or the greatest of three dimensions of an object
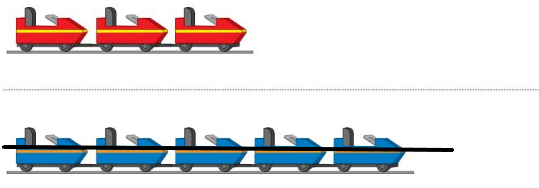
Lesson 13.4 Compare Weights
Explore and Grow
Directions: Cut out the Weight Sort Cards. Compare the objects to the lion shown. Then sort the cards into the categories shown.
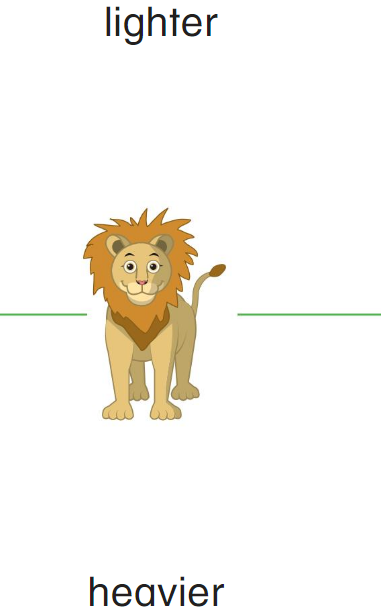
Answer:
The elephant is heavier and the mouse is lighter.
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight

Think and Grow
Directions: Compare the weights of the objects.
• Circle the heavier object.
• Draw a line through the lighter object.
• Are the markers the same weight? Circle the thumbs up for yes or the thumbs down for no.

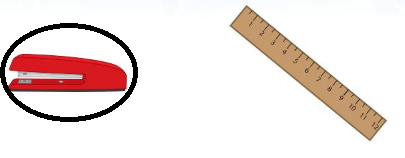
Answer:
stapler is heavier than measuring tape
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
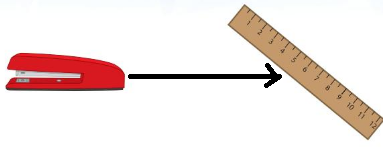
step 2:
Line through lighter object
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight

Answer:
Yes, the markers are same weight.
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight

Apply and Grow: Practice
Directions:
1 and 2 Circle the heavier object. 3 and 4 Draw a line through the lighter object. 5 Are the objects the same weight? Circle the thumbs up for yes or the thumbs down for no.
Question 1.

Answer:
crayon box is heavier than one crayon
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight

Question 2.

Answer:
circled the heavier object
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight

Question 3.

Answer:
Line drawn through the lighter object.
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
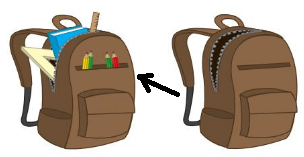
Question 4.

Answer:
line drawn through the lighter object.
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight

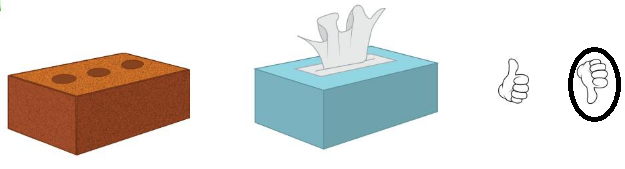
Question 5.
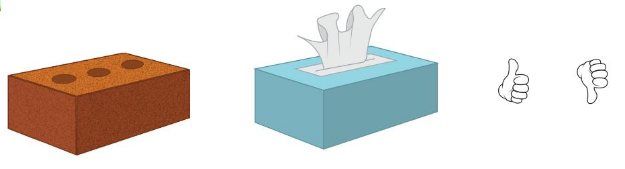
Answer:
Brick is heavier than the tissue box
so, they are not equal
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Directions:
• Circle the object you can carry. Tell why you can carry the object.
• Circle the object you cannot carry. Tell why you cannot carry the object.
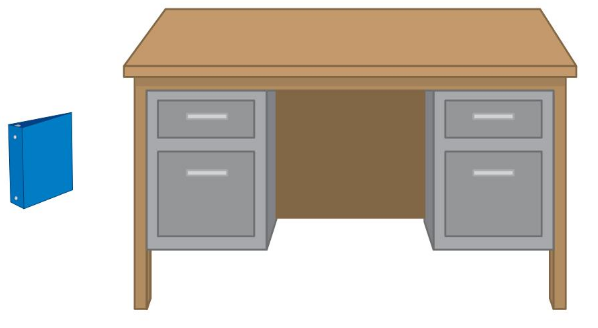
Answer:
The folder is lighter in weight in can be easily carried
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
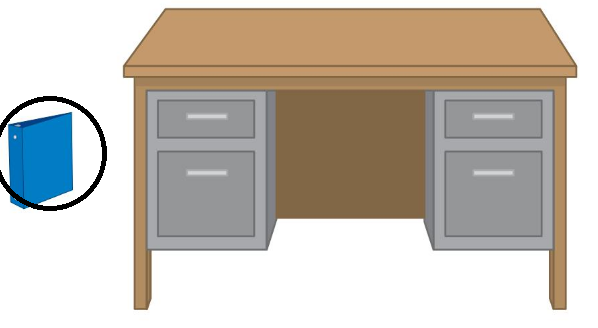

Answer:
The bus cannot be carried because it heavier in weight
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight

Compare Weights Homework & Practice 13.4
Directions:
1 and 2 Circle the heavier object. 3 and 4 Draw a line through the lighter object.
Question 1.

Answer: The chair is heavier than the glue
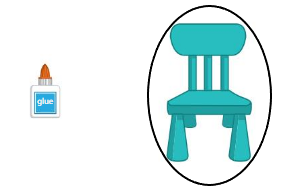
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
Question 2.
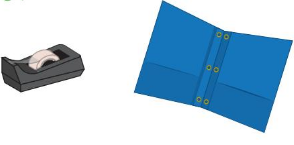
Answer:
The line drawn through the file
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
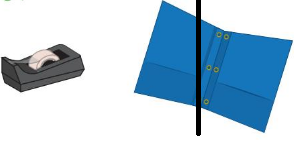
Question 3.

Answer:
Line drawn through the lighter object

Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
Question 4.

Answer:
Line drawn through the lighter object.
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight

Directions:
5 and 6 Are the objects the same weight? Circle the thumbs up for yes or the thumbs down for no. 7 Circle the object you can carry. Tell why you can carry the object.
Question 5.

Answer:
Both the objects are same weight
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight

Question 6.

Answer:
Both the objects are not in equal weight
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight

Question 7.
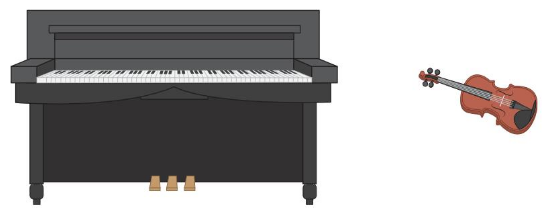
Answer:
We can carry the violin because it is lighter in weight
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
Lesson 13.5 Use Numbers to Compare Weights
Explore and Grow
Directions: Hold some counting bears in one hand and a different amount of counting bears in your other hand. Place the groups of bears on the correct buckets on the scale.
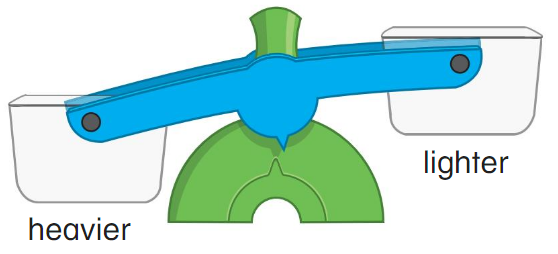
Think and Grow
Directions:
• Compare the weights of the groups of linking cubes. Match each group of linking cubes with the correct side of the balance.
• Compare the weights of the groups of linking cubes. Match each group of linking cubes with the correct side of the balance.
• Circle the number of linking cubes that makes the balance scale even.
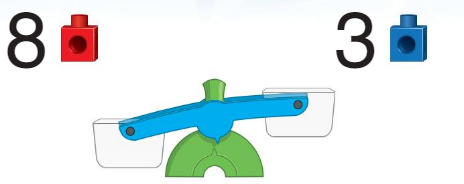
Answer:
Each group of linking measures show the correct sides
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
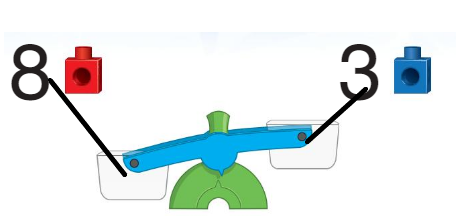
Answer:
Does not show the equal measures
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
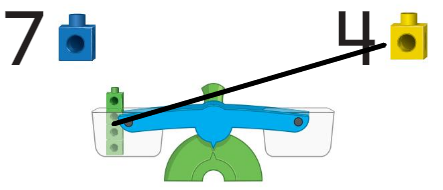
Apply and Grow: Practice
Directions:
1 – 3 Compare the weights of the groups of linking cubes. Match each group of linking cubes with the correct side of the balance scale.
Question 1.
Answer:
when weight is more the machine goes down and which has less weight it comes up.
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
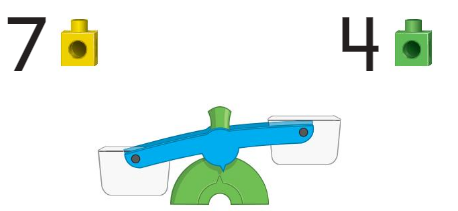
Question 2.
6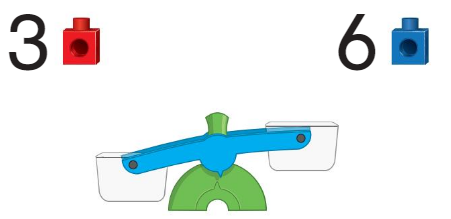
Answer:
The three side should be up as it has less weight and 6 should be down as it has more weight.
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
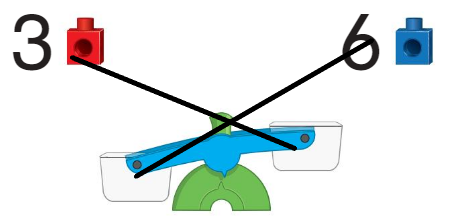
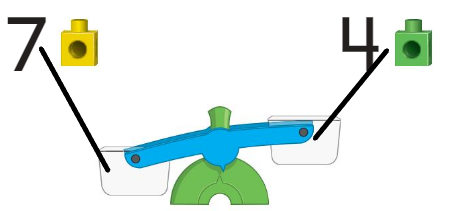
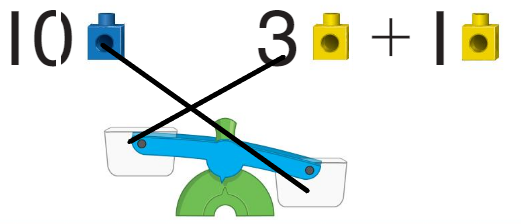
Question 3.
Answer:
10 should be down as it has the more weight and 3 + 1 =4 should be up as it has less weight.
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Directions:
• Circle the basket that is lighter. Tell how you know.
• Circle the basket that is heavier. Tell how you know.
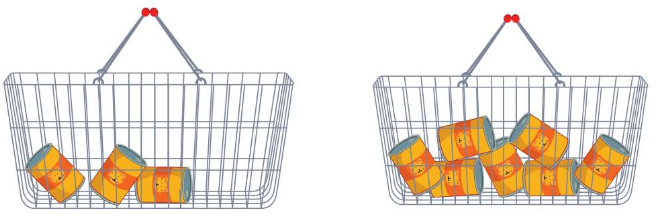
Answer:
First basket is lighter in weight because number of bottles in first basket is less than the second one
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
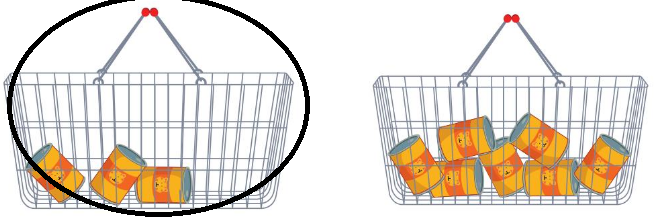
Answer:
The first one is heavier because the number of bottle in the first basket is more than the second basket.
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
Use Numbers to Compare Weights Homework & Practice 13.5
Directions:
1 and 2 Compare the weights of the groups of linking cubes. Match each group of linking cubes with the correct side of the balance scale.
Question 1.
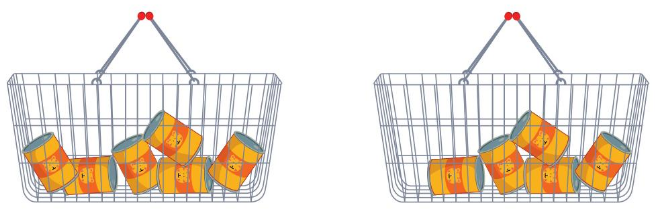
Answer:
As 5 has more linking cubes than 1, 5 should be down and 1 should be up.
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
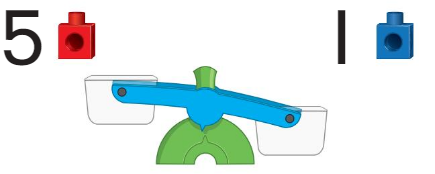
Question 2.
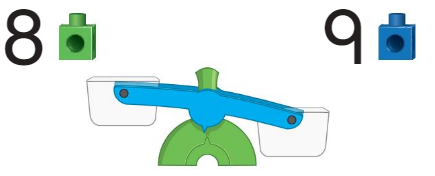
Answer:
The weighing measure shows correct measures.
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
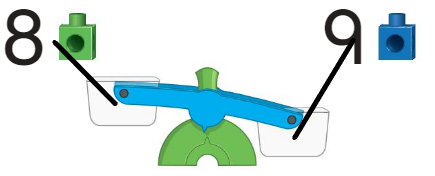
Directions:
3 Compare the weights of the groups of linking cubes. Match each group of linking cubes with the correct side of the balance scale. 4 Circle the Circle the basket number of linking cubes that makes the balance scale even. 5 Circle the basket that is heavier. Tell how you know.
Question 3.
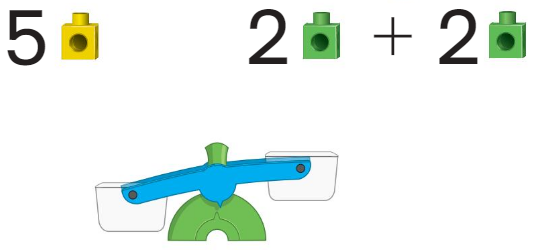
Answer:
2 + 2 = 4 is lighter and 5 is heavier,
5 will be down and and 4 will be up
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
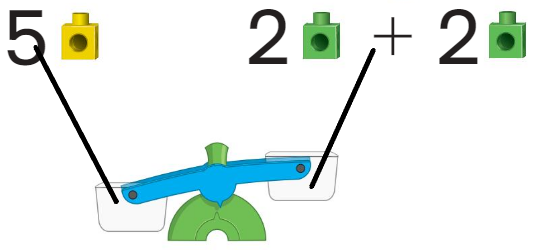
Question 4.
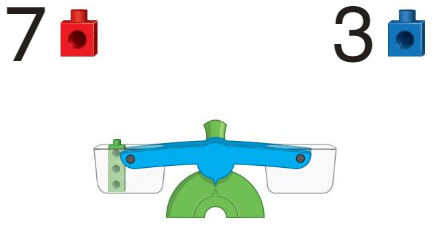
Answer: Line drawn through the correct measures
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
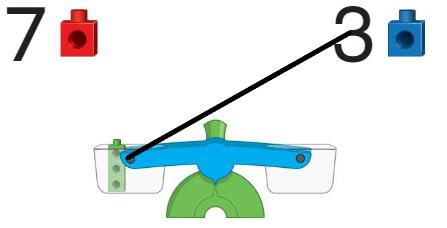
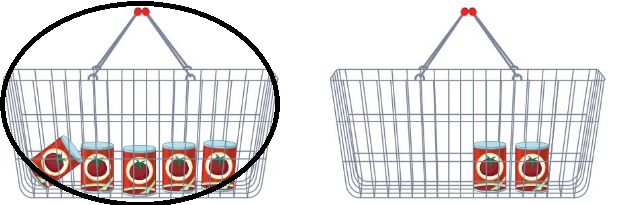
Question 5.
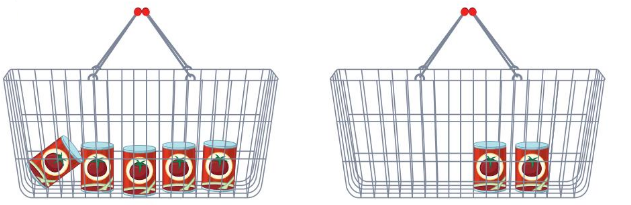
Answer:
The first basket is heavier than the second one
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
Lesson 13.6 Compare Capacities
Explore and Grow
Directions: Cut out the Capacity Sort Cards. Compare the objects to the bucket shown. Then sort the cards into the categories shown.
Think and Grow
Directions: Compare the capacities of the objects.
• Circle the object that holds more.
• Draw a line through the object that holds less.
• Do the recycling bins hold the same amount? Circle the thumbs up for yes or the thumbs down for no.

Answer: The cup contains the more
Explanation:
The maximum amount that something can contain
The maximum is that holds more
and the minimum that holds less

Answer:
The recycling bins hold the same amount
Explanation:
The maximum amount that something can contain
The maximum is that holds more
and the minimum that holds less

Apply and Grow: Practice
Directions:
1 and 2 Circle the object that holds more. 3 and 4 Draw a line through the object that holds less. 5 Do the milk containers hold the same amount? Circle the thumbs up for yes or the thumbs down for no.
Question 1.

Answer:
The bag contains the more amount
Explanation:
The maximum amount that something can contain
The maximum is that holds more
and the minimum that holds less
Question 2.
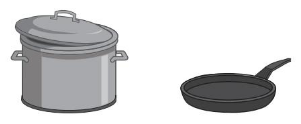
Answer:
The container contains more amount
Explanation:
The maximum amount that something can contain
The maximum is that holds more
and the minimum that holds less
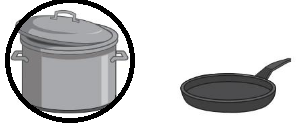
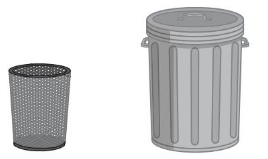
Question 3.
Answer:
second figure holds the less
Explanation:
The maximum amount that something can contain
The maximum is that holds more
and the minimum that holds less
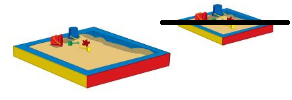
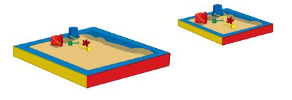
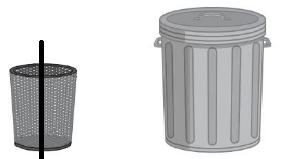
Question 4.
Answer:
line drawn through the object which contain less
Explanation:
The maximum amount that something can contain
The maximum is that holds more
and the minimum that holds less
Question 5.

Answer:
The milk container does not contain the equal amount
Explanation:
The maximum amount that something can contain
The maximum is that holds more
and the minimum that holds less

Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Directions:
• You are going camping. Circle the backpack that can hold all of your camping supplies. Tell how you know.
• You are going to school. Circle the bag that cannot hold all of your school supplies. Tell how you know.

Answer:
Circled the backpack that holds all of your camping supplies.
The second bag holds all the things.
Explanation:
The maximum amount that something can contain
The maximum is that holds more
and the minimum that holds less

Answer:
Circled the bag that cannot hold all of your school supplies.
Explanation:
The maximum amount that something can contain
The maximum is that holds more
and the minimum that holds less

Compare Capacities Homework & Practice 13.6
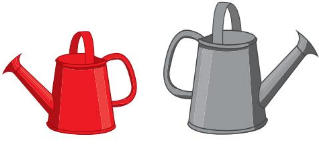
Directions: 1 and 2 Circle the object that holds more. 3 and 4 Draw a line through the object that holds less.
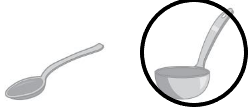
Question 1.

Answer:
The second spoon contains the more amount.
Explanation:
The maximum amount that something can contain
The maximum is that holds more
and the minimum that holds less
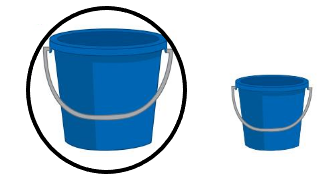
Question 2.

Answer:
The Big bucket contains the more amount
Explanation:
The maximum amount that something can contain
The maximum is that holds more
and the minimum that holds less
Question 3.
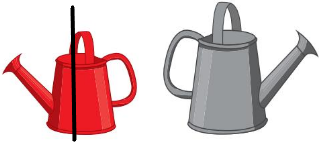
Answer:
Line Drawn through the shorter object
Explanation:
The maximum amount that something can contain
The maximum is that holds more
and the minimum that holds less
Question 4.

Answer:
Line drawn through the shorter object
Explanation:
The maximum amount that something can contain
The maximum is that holds more
and the minimum that holds less

Directions:
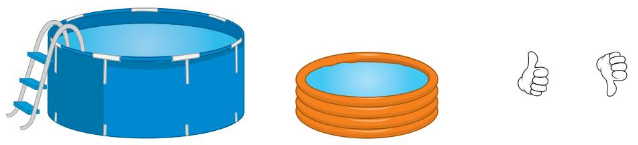
5 and 6 Do the objects hold the same amount? Circle the thumbs up for yes or the thumbs down for no. 7 Your class is going on a field trip. Circle the vehicle that can hold your class. Tell how you know.
Question 5.

Answer:
Both the basket contains the same amount
Explanation:
The maximum amount that something can contain
The maximum is that holds more
and the minimum that holds less

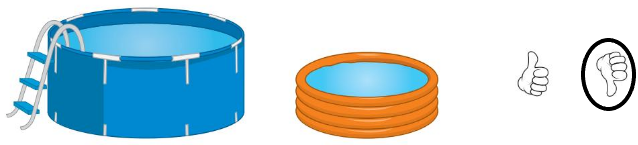
Question 6.
Answer:
The objects does not contain the same amount
Explanation:
The maximum amount that something can contain
The maximum is that holds more
and the minimum that holds less
Question 7.

Answer:
The bus can hold all the children
Explanation:
The maximum amount that something can contain
The maximum is that holds more
and the minimum that holds less
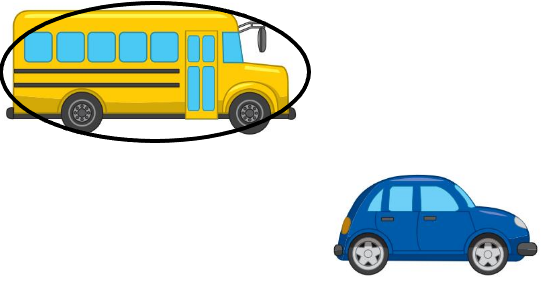
Lesson 13.7 Describe Objects by Attributes
Explore and Grow
Directions: Cut out the Measurable Attribute Sort Cards. Place the objects that you can measure using length or height into the length or height box. Then place the objects that you can measure using weight into the weight box. Then place the objects that you can measure using capacity into the capacity box.
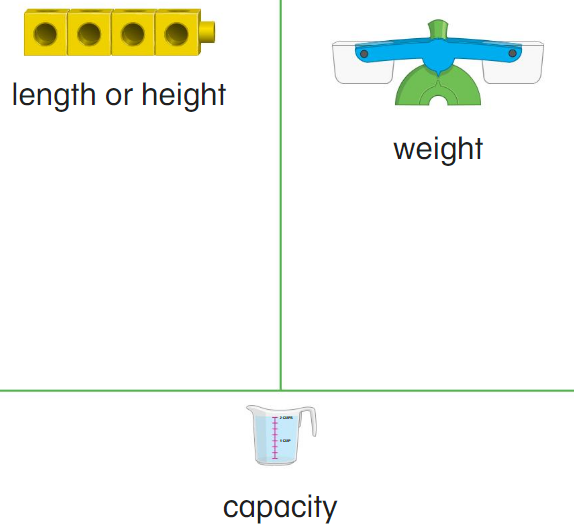
Think and Grow
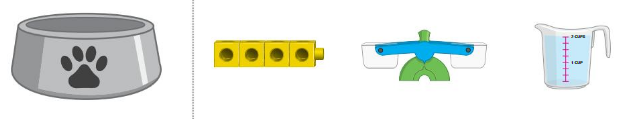
Directions: Circle the measurable attributes of the object
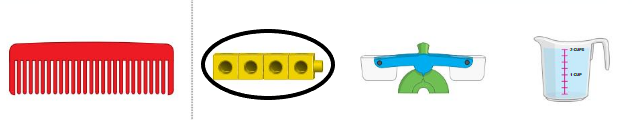
Answer:
cubes are the measuring attribute
Explanation:
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
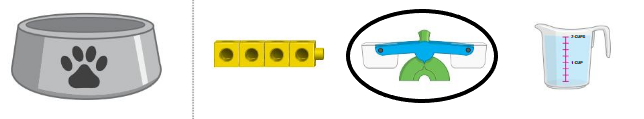
Answer:
weighing machine is the measuring attribute
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
Answer:
Capacity is the measuring attribute
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
Apply and Grow: Practice
Directions:
1– 4 Circle the measurable attributes of the object. 5 Circle the objects that have capacity as an attribute.
Question 1.

Answer:
cubes are the measuring attribute
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers

Question 2.
Answer:
weighing is the measuring attribute
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
Question 3.
Answer:
cubes are the measuring attribute
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
Question 4.
Answer:
cubes are the measuring attribute
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
Question 5.

Answer:
The glue is the capacity attribute
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers

Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Directions:
• Draw an object that has capacity as an attribute.
• Draw an object that does not have capacity as an attribute.


Answer:
Jar is the capacity object
pencil is not the capacity object
Explanation:
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
Describe Objects by Attributes Homework & Practice 13.7
Directions:
1 – 3 Circle the measurable attributes of the object.
Question 1.
Answer:
Cubes are the measuring object
Explanation:
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
Question 2.
Answer:
cubes are the measuring object
Explanation:
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
Question 3.
Answer:
cube is the measuring object
Explanation:
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
Directions:
4 Circle the measurable attributes of the broccoli. 5 Circle the objects that have length as an attribute. 6 Draw an object that has length as an attribute. 7 Draw an object that has weight as an attribute.
Question 4.
Answer:
Weighing is the measuring attribute
Explanation:
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
Question 5.
Answer:
fork, tree, toy helicopter are length attributes
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
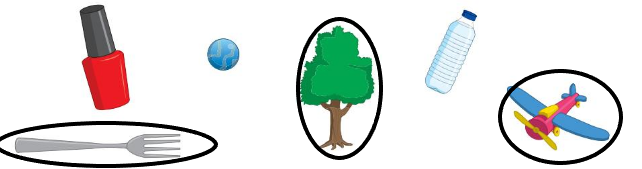
Question 6.

Answer:
fork is the length attribute
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
![]()
Question 7.
Answer:
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
water bottle is the capacity attribute

Measure and Compare Objects Performance Task
Directions: You use one bucket to collect rainwater on Monday and a different bucket to collect rainwater on Tuesday. On Monday, you collect 1 less than 7 fluid ounces of rainwater. On Tuesday, you collect 1 more than 3 fluid ounces of rainwater. 1 Circle the number on each bucket that shows the amount of rainwater you collect. Then circle the day that you collect more rainwater. 2 Draw a bucket for Wednesday that is taller and holds more water than Monday’s bucket. 3 The amount of rainwater you collect on Wednesday is the same as the amount you collect in all on Monday and Tuesday. Write an addition sentence to tell how much rainwater you collect on Wednesday.
Question 1.
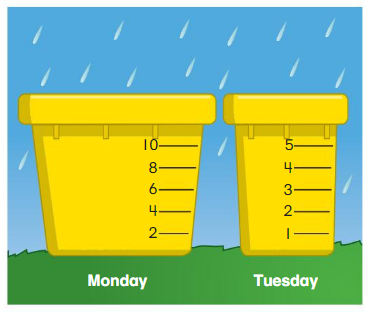
Answer:
Question 2.

Answer: the diagram is shown below.
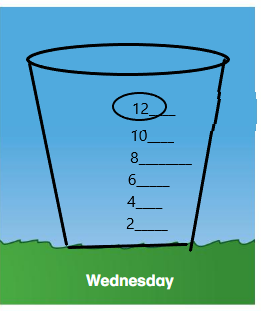
Question 3.

Answer:
1 less than 7 fluid ounces of rainwater = 6
1 more than 3 fluid ounces of rainwater = 4
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
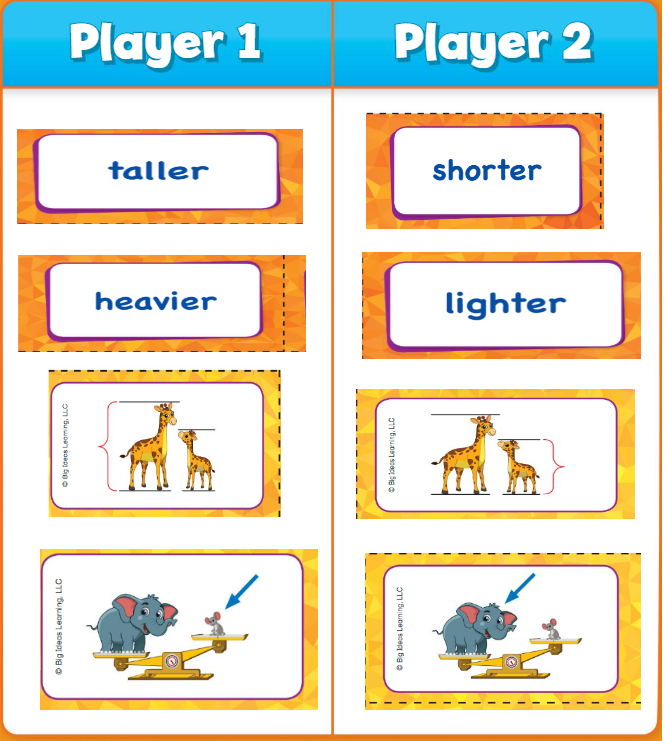
Measure and Compare Objects Activity
Measurement Boss
Directions: Each player flips a Measurement Boss Card and places it on the page. Compare the objects based on the attribute of the card. The player with the object that is longer, taller, heavier, or holds more takes both cards. Repeat until all cards have been used.

Measure and Compare Objects Chapter Practice
Directions:
1 and 2 Circle the taller object. 3 Draw a line through the shorter object. 4 Are the crayons the same length? Circle the thumbs up for yes or the thumbs down for no. 5 Draw a string that holds the same number of beads as the string shown. Tell how you know.
13.1 Compare Heights
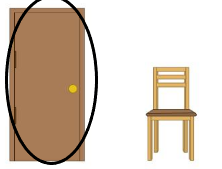
Question 1.

Answer:
The door is taller than the chair
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
Question 2.

Answer:
The dog is taller than the cat
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.

13.2 Compare Lengths
Question 3.
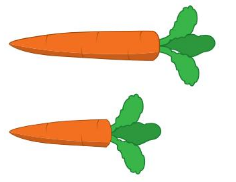
Answer:
Line drawn through the shorter object
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
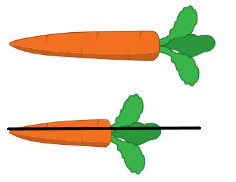
Question 4.
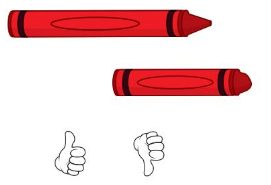
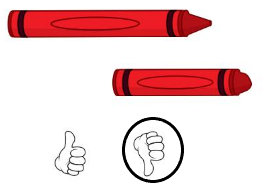
Answer: second crayon is shorter.
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
Question 5.

Answer:
string drawn with equal length.
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.

Directions:
6 and 7 Compare the lengths of the cube trains that have the given number of cubes. Circle the number of the train that is longer. Color to show how you know. 8 Draw a line through the lighter object. Are the footballs the same weight? 9 Circle the thumbs up for yes or the thumbs down for no.
13.3 Use Numbers to Compare Lengths
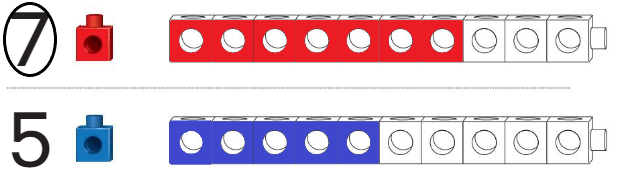
Question 6.
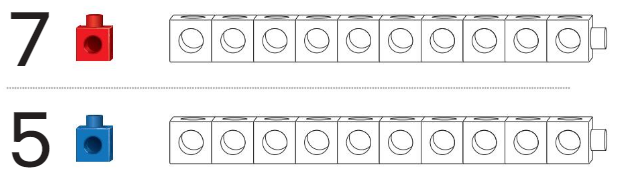
Answer:
7 is the bigger train than the 5
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
the measurement or extent of something from end to end; the greater of two or the greatest of three dimensions of an object
Question 7.
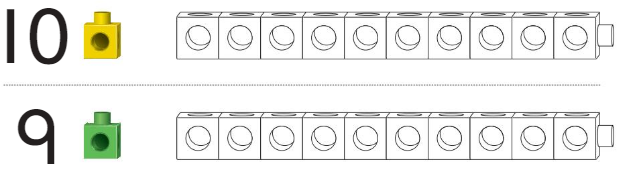
Answer:
10 train is lengthier than the 9
Explanation:
Great or more than average height,
especially (with reference to an object) relative to width and height
measuring a specified distance from top to bottom.
the measurement or extent of something from end to end; the greater of two or the greatest of three dimensions of an object
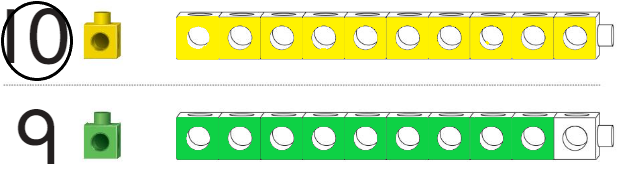
13.4 Compare Weights
Question 8.
Answer:
Line drawn through the lighter object
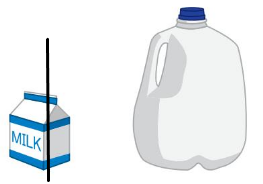
Question 9.

Answer: Yes, the foot balls are same weight
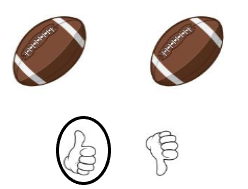
Directions:
10 Compare the weights of the groups of linking cubes. Match each group of linking cubes with the correct side of the balance scale. 11 Circle the bag that is lighter. Tell how you know. 12 and 13 Draw a line through the object that holds less.
13.5 Use Numbers to Compare Weights
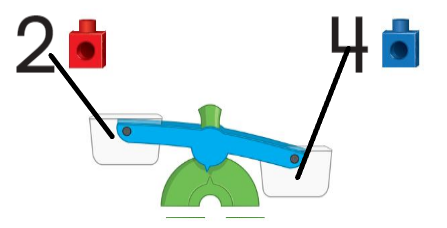
Question 10.
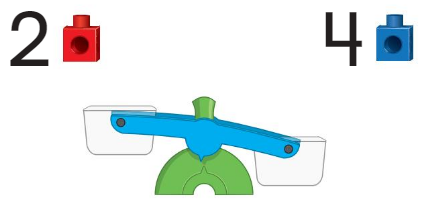
Answer: 4 comes down and 2 goes up
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
.
Question 11.
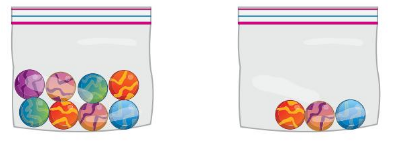
Answer: The bag that contains 3 balls are lighter.
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight

13.6 Compare Capacities
Question 12.
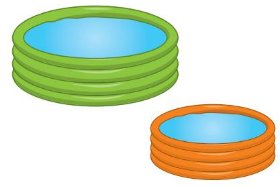
Answer: Line drawn through the lighter object.
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight
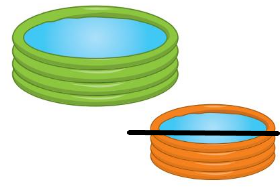
Question 13.

Answer: Line drawn through the lighter object.
Explanation:
heavier of great weight; difficult to lift or move
of great density; thick or substantial
lighter than the expected item or which weighs less weight

Directions:
14 Do the water bottles hold the same amount? Circle the thumbs up for yes or the thumbs down for no. 15 – 17 Circle the measurable attributes of the object. 18 Circle the objects that have capacity as an attribute.
Question 14.

Answer: The water bottles does not hold the same amount of water.

13.7 Describe Objects by Attributes
Question 15.
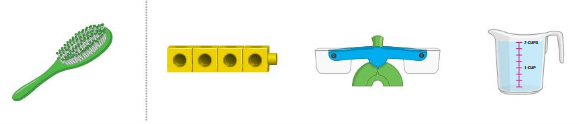
Answer:
Cubes are the measuring attribute of length.
Explanation:
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
Question 16.
Answer:
capacity is the measuring attribute.
Explanation:
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
Question 17.
Answer:
It can be measured with cubes length attribute.
Explanation:
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
Question 18.

Answer:
Circled the measuring attribute.
Explantion:
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers

Measure and Compare Objects Cumulative Practice
Directions:
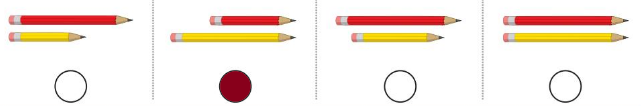
Shade the circle next to the answer. 1 Which group has a yellow pencil that is longer than the red pencil? 2 Which five frame shows how many sharks are in the picture? 3 Which group has all rectangles?
Question 1.
Answer:
Second picture has yellow longer.
Explanation:
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
Question 2.
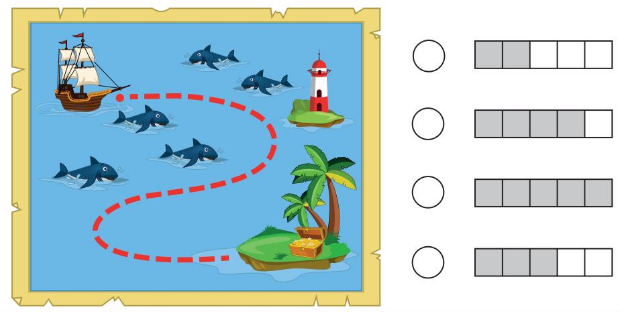
Answer:
There are 5 sharks in the picture.
Explanation:
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
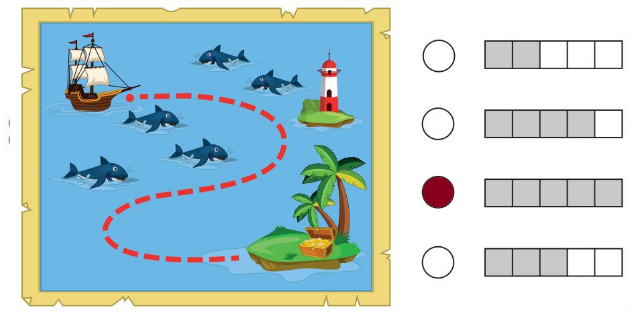
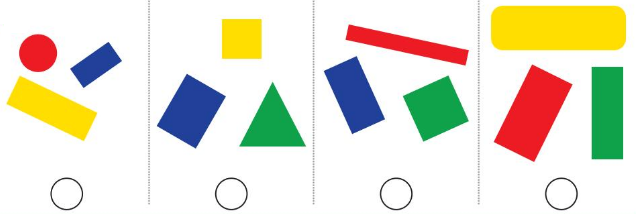
Question 3.
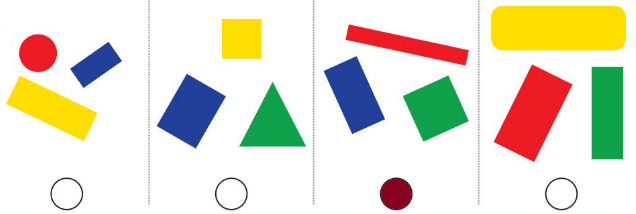
Answer:
The third image shows all rectangles
Explantion:
The attributes we measure come in two main types, quantitative and categorical. Quantitative attributes are attributes we measure using numbers. For example, your height is a quantitative attribute. On the other hand, a categorical attribute is something measured without using numbers
Directions:
Shade the circle next to the answer. 4 Which subtraction sentence not tells how many geese are left? 5 Which shape is a solid shape? 6 Which solid shape does not stack or slide?
Question 4.
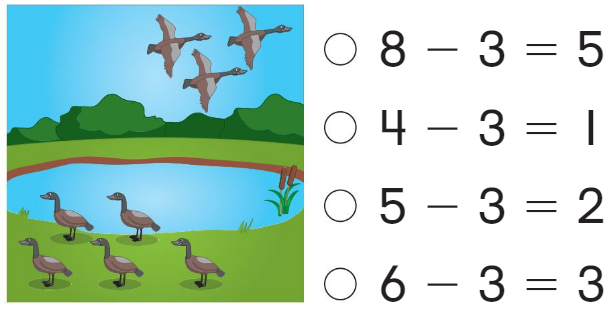
Answer:
the first substraction sentence shows
Explanation:
There are 8 birds 3 are flying and 5 are sitting
and the picture shows 8 – 3 = 5
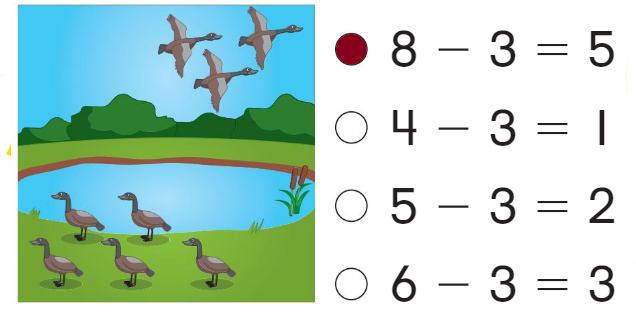
Question 5.
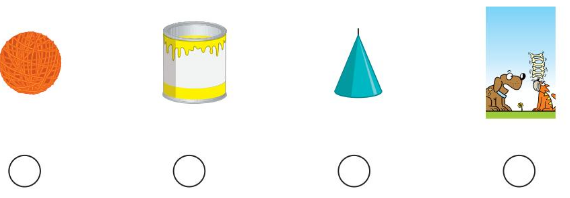
Answer:
The pyramid shows the solid shape
Explanation:
Solid Shapes. Objects that occupy space are called solid shapes. Their surfaces are called faces. Faces meet at edges and edges meet at vertices. Some examples of solid shapes: Cone, Cuboid, Sphere, Cylinder, Cube
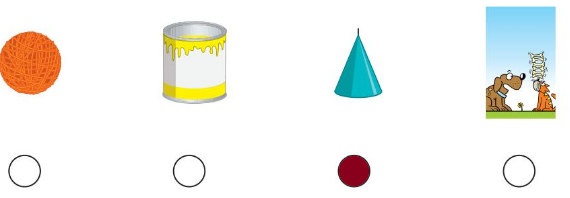
Question 6.
Answer:
the box will not slide or stack
Explanation:
Solid Shapes. Objects that occupy space are called solid shapes. Their surfaces are called faces. Faces meet at edges and edges meet at vertices. Some examples of solid shapes: Cone, Cuboid, Sphere, Cylinder, Cube
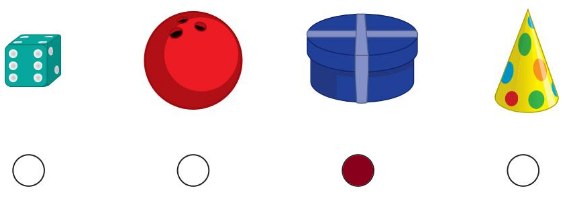
Directions:
7 Circle the objects that have capacity as an attribute. 8 Circle the object that looks like a cylinder that is above the ball. 9 Find the number of dots on each domino. Write each number. Draw a line through the number that is less than the other number.
Question 7.

Answer: The aquarium is capacity attribute.
Explanation:
Capacity Attributes means any and all current or future defined characteristics, certificates, tag, credits, ancillary service attributes, or accounting construct

Question 8.

Answer:
Nothing shows like a cylinder above the ball.
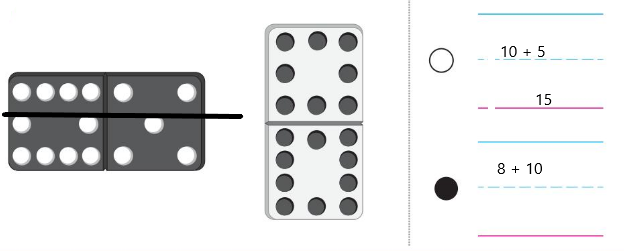
Question 9.
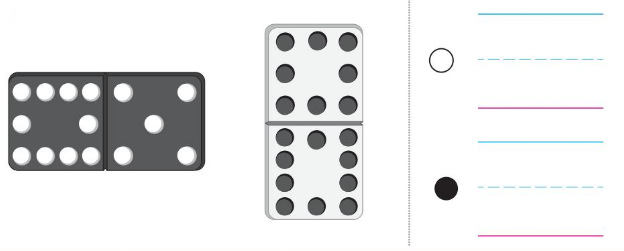
Answer:
Line drawn through the less number.
Explanation:
10 + 5 = 15
8 + 10 = 18
line drawn through the dice
Directions:
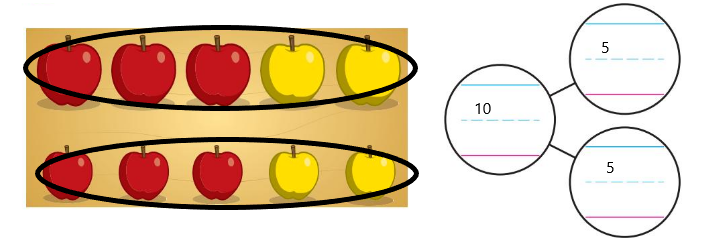
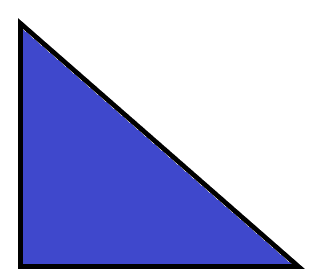
10 Trace the shapes that are hexagons. Write the number of sides and the number of vertices of a hexagon. 11 You have 10 apples. Classify the apples into 2 categories. Circle the groups. Then complete the number bond to match your picture. 12 Draw a larger triangle that can be formed by the 2 triangles shown.
Question 10.
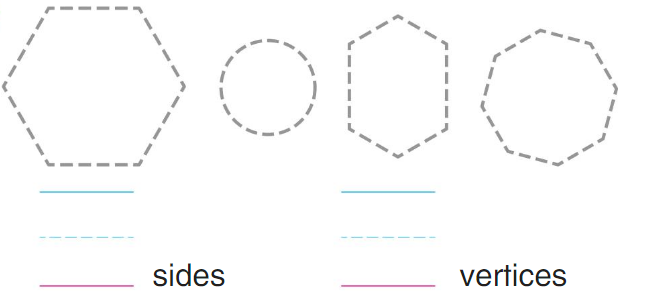
Answer:
there are two hexagons of 6 sides and 6 vertices.
Explanation:
a plane figure with six straight sides and angles
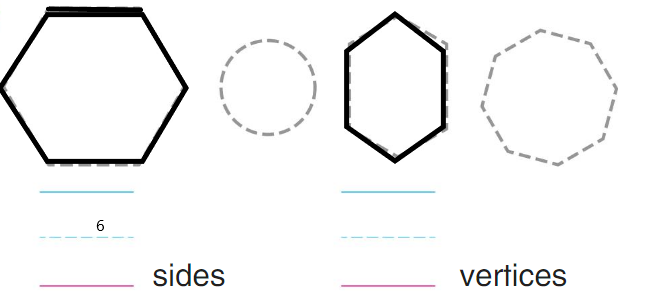
Question 11.
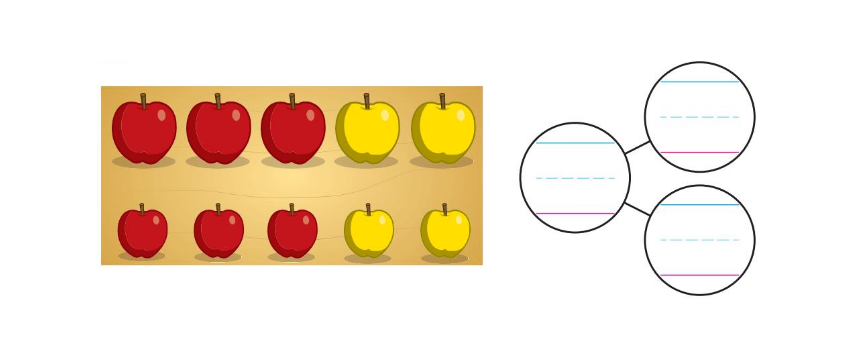
Answer:
The apples are made into 2 groups of 5 each.
Explanation:
the total ten apples are made in to 2 groups 5 in each group
3 are red and big 2 are yellow and small
3 are red and small and 2 are yellow and small.
Question 12.

Answer:
Drawn a big triangle with the help of two triangles
Explanation:
A triangle has 3 sides and 3 vertices
with equal length
Conclusion:
Hence make your children ready by making them practice for the test using Big Ideas Math Book Grade K Answer Key Chapter 13 Measure and Compare Objects. Get the solutions for all the questions with the simple tricks for all chapters on Big Ideas Math Answer Key. Best Of Luck!!!