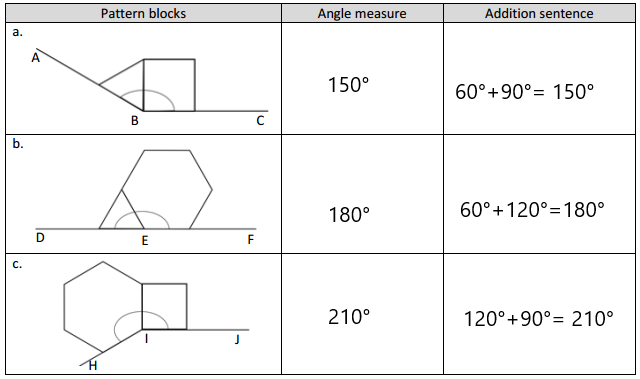
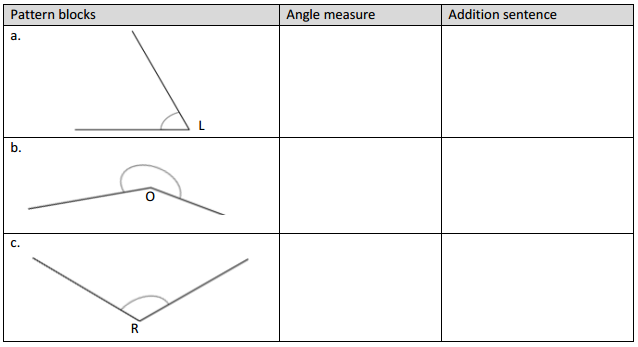
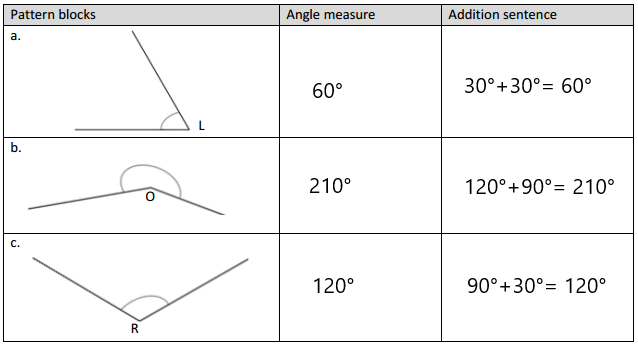
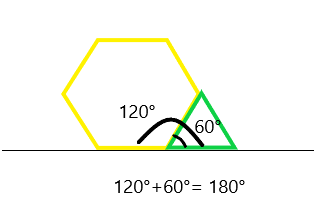
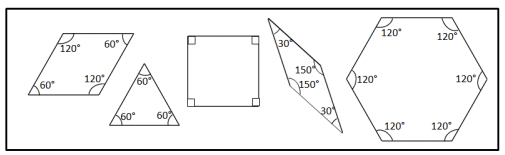
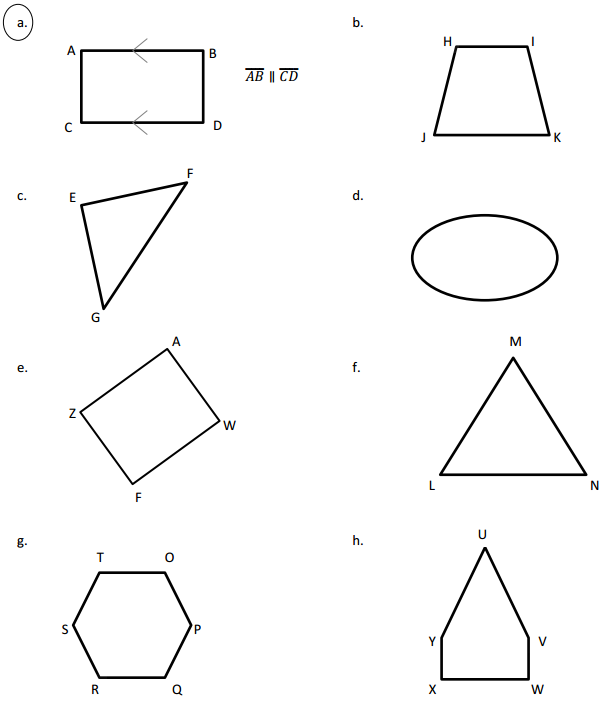
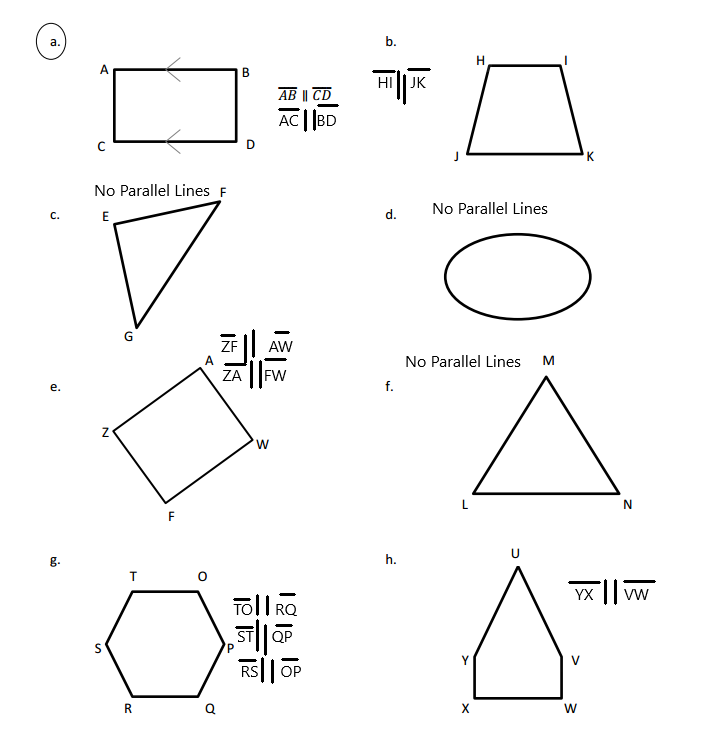
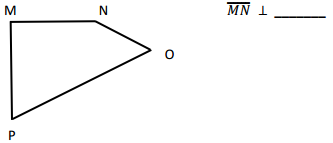
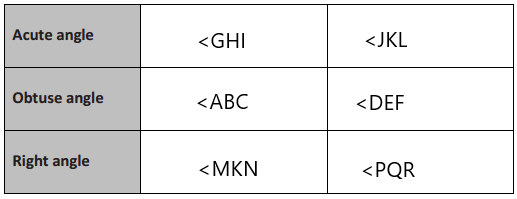
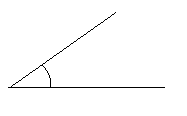
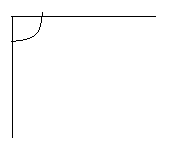
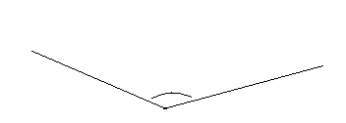
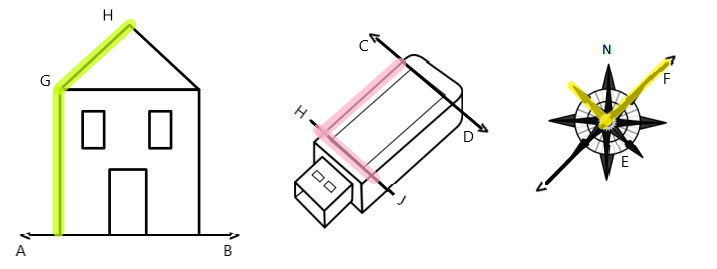
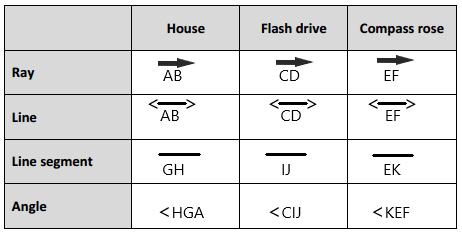
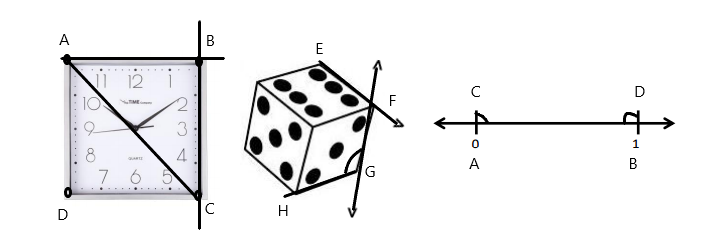
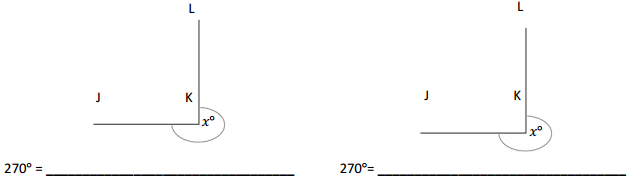Engage NY Eureka Math 4th Grade Module 4 Lesson 11 Answer Key
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 4 Lesson 11 Problem Set Answer Key
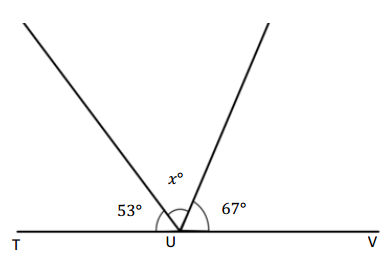
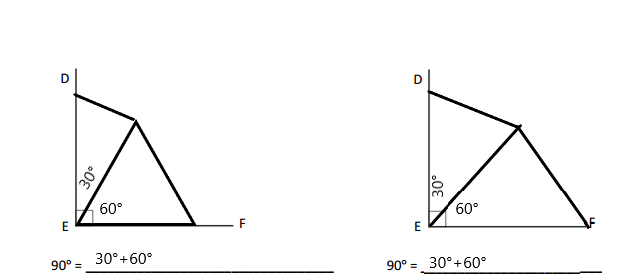
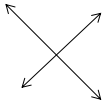
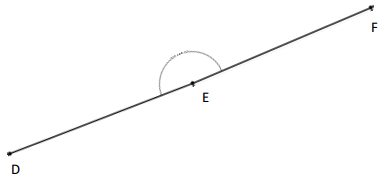
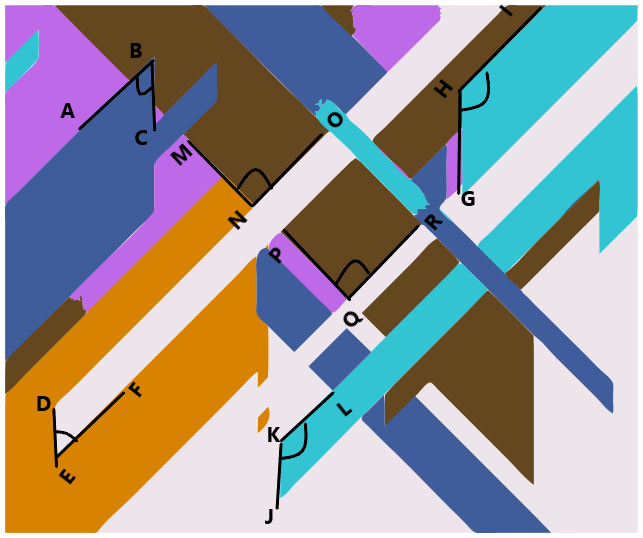
Write an equation, and solve for the unknown angle measurements numerically.
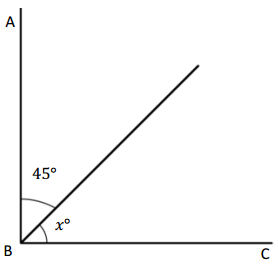
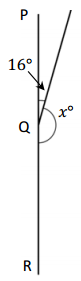
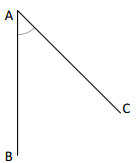
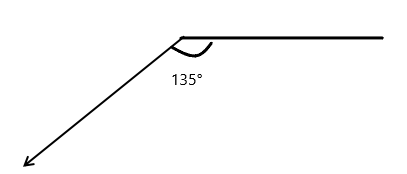
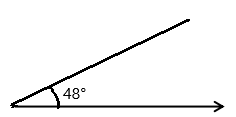
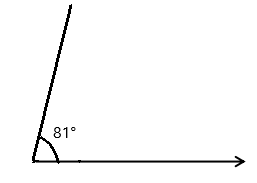
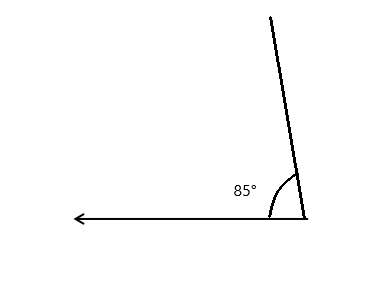
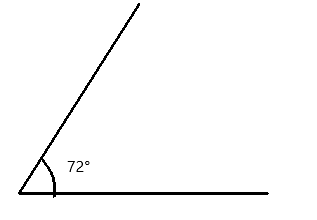
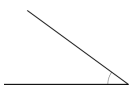
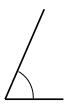
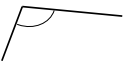
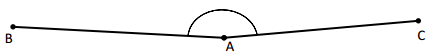
Question 1.
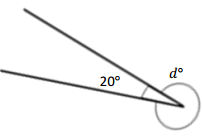
______° + 20° = 30°
d° = ______°
Answer:
The value of d° is 10°.
Explanation:
Given that the value of the angle acute angle is 30° and the value of the other angle is 20° and the value of another angle is d°. So the equation will be
d° + 20°= 30°
so the value of d° is 30° – 20°
= 10°.
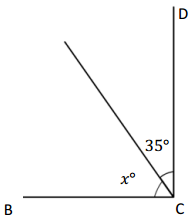
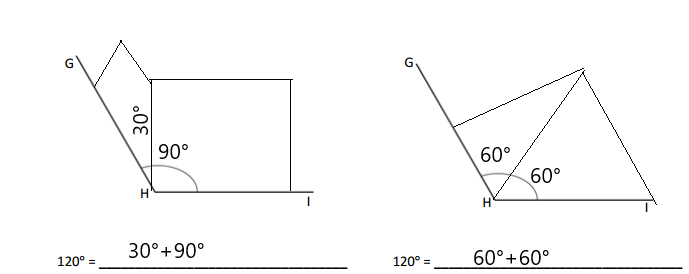
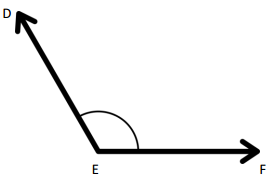
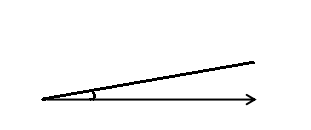
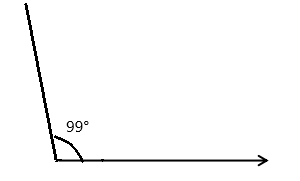
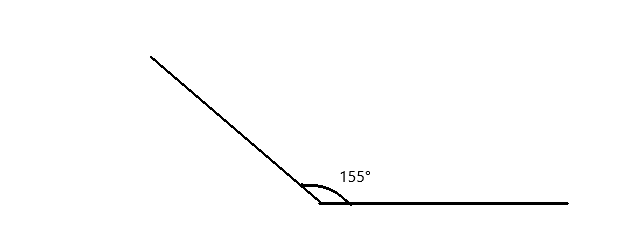
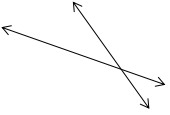
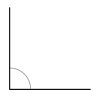
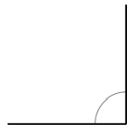
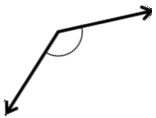
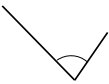
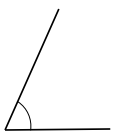
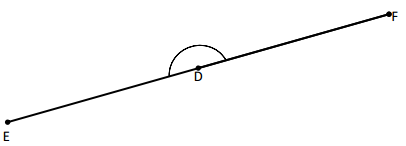
Question 2.
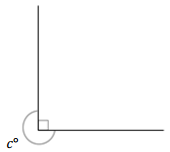
______° + ______°= 360°
c° = ______°
Answer:
The value of c° is 270°.
Explanation:
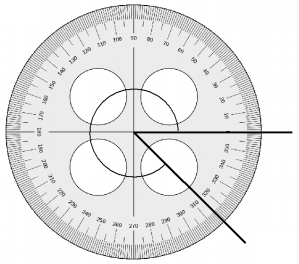
Here, in the above image, we can see that an arc that represents a complete rotation which means 360°, and the other angle 90°. So the equation will be c°+90°= 360° and the value of c° is
c°= 360°-90°
= 270°.
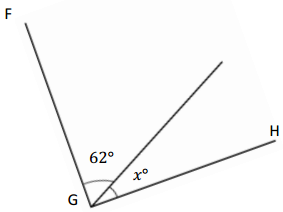
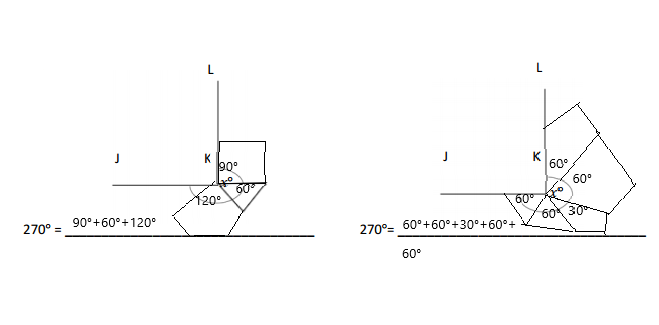
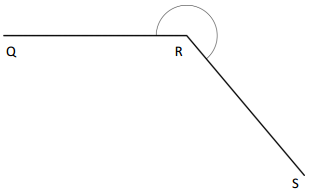
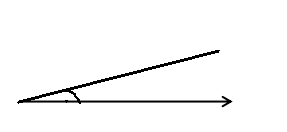
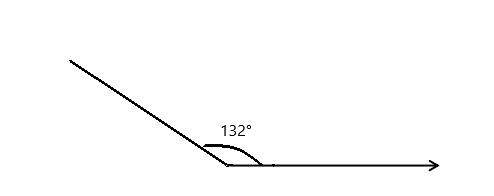
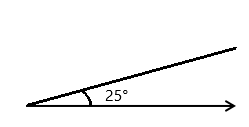
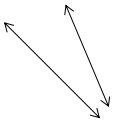
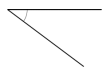
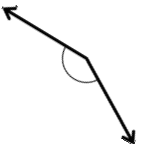
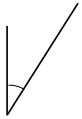
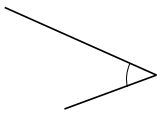
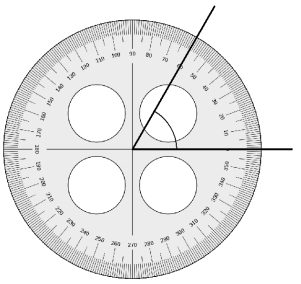
Question 3.
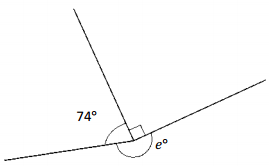
______° + ______° + ______° = ______°
e° = ______°
Answer:
The value of e° is 196°.
Explanation:
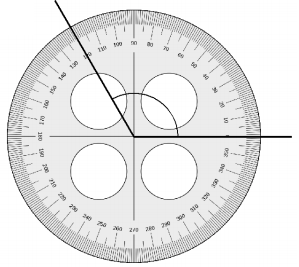
Here we will measure the angles using a protractor and the values of the angles will be 90° and 196°. So the equation will be 74°+90°+e°= 360° and the value of e is
e° = 360°- 164°
= 196°.
So the value of e° is 196°.
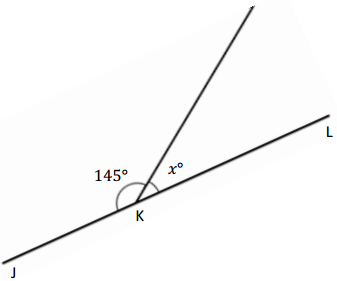
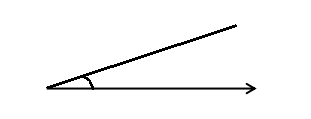
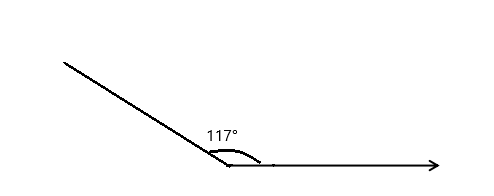
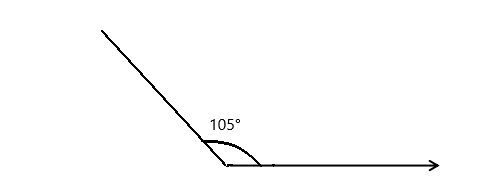
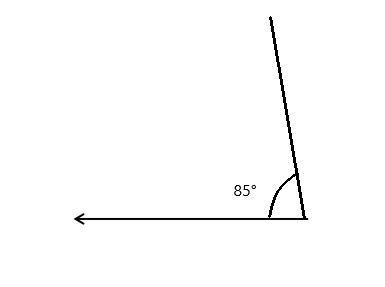
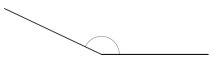
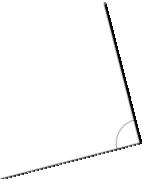
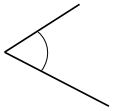
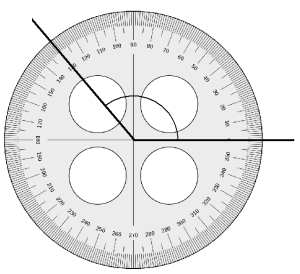
Question 4.
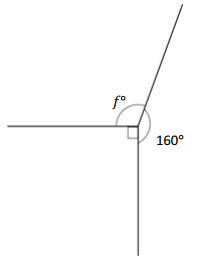
______° + ______° + ______° = ______°
f° = ______°
Answer:
The value of f° is 110°.
Explanation:
Here we will measure the angles using a protractor and the values of the angles will be 90° and 160°. So the equation will be 90°+160°+f°= 360° and the value of f is
f° = 360°- 250°
= 110°.
So the value of f° is 110°.
Write an equation, and solve for the unknown angles numerically.
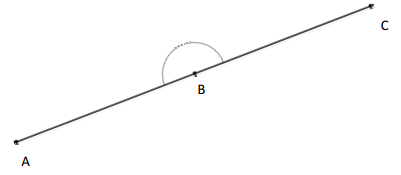
Question 5.
O is the intersection of \(\overline{A B}\) and \(\overline{C D}\). ∠DOA is 160°, and ∠AOC is 20°.
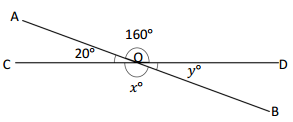
x° = ______° y° = ______°
Answer:
The value of x° is 160°.
The value of y° is 20°.
Explanation:
In the above image, we can see that the angle COD is 180° and <DOA is 160° and <AOC is 20°. So the equation will be 160° + y°= 180° and the value of y°= 180° – 160°
y°= 20°.
So the value of y° is 20°.
And the other equation will be 20° + x°= 180°
x°= 180° – 20°
= 160°.
So the value of the x°is 160°.
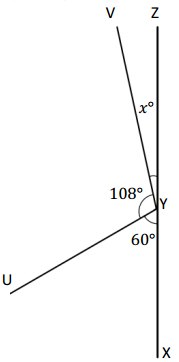
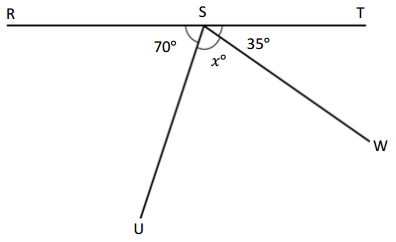
Question 6.
O is the intersection of \(\overline{R S}\) and \(\overline{T V}\). ∠TOS is 125°.
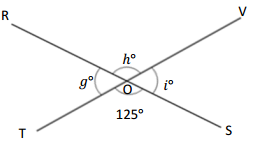
g° = ______° h° = ______° t° = ______°
Answer:
The value of i° is 55°.
The value of h° is 125°.
The value of g° is 55°.
Explanation:
In the above image, we can see that the angle TOV is 180° and angle SOR is 180° and <TOS is 125°. So the equation will be 125° + i°= 180° and the value of i°= 180° – 125°
i°= 55°.
So the value of i° is 55°.
And the other equation will be 55° + h°= 180°
h°= 180° – 55°
= 125°.
So the value of the h°is 125°.
And the other equation will be 125° + g°= 180°
g°= 180° – 125°
= 55°.
So the value of the g°is 55°.
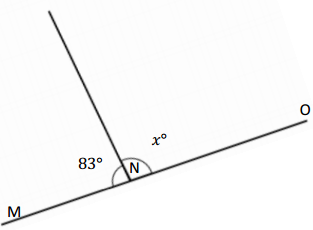
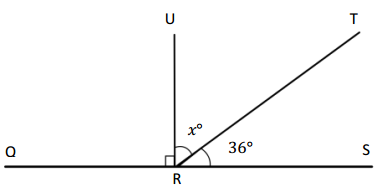
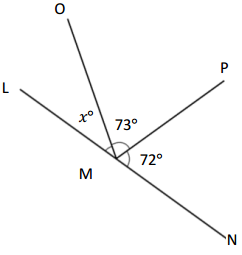
Question 7.
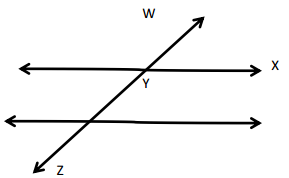
O is the intersection of \(\overline{W X}\), \(\overline{Y Z}\), and \(\overline{U O}\) ∠XOZ is 36°
k° = ______° m° = ______° n° = ______°
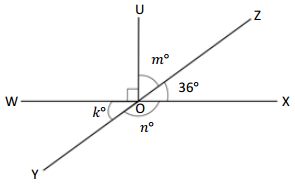
Answer:
The value of m° is 54°.
The value of k° is 36°.
The value of n° is 144°.
Explanation:
In the above image, we can see that the angle WOX is 180° and angle XOZ is 36°, and the value of angle UOX is 90°. So the equation will be 90°+m+ 36°= 180° and the value of m°= 180° – 126°
m°= 54°.
So the value of m° is 54°.
And the other equation will be 54° +90°+k°= 180°
k°= 180° – 144°
= 36°.
So the value of the k°is 36°.
And the other equation will be 36° +n°= 180°
n°= 180° – 36°
= 144°.
So the value of the n°is 144°.
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 4 Lesson 11 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Write equations using variables to represent the unknown angle measurements. Find the unknown angle measurements numerically.
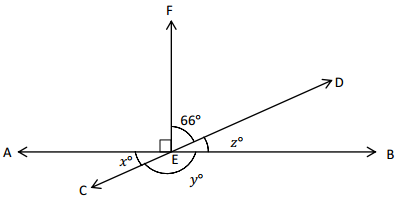
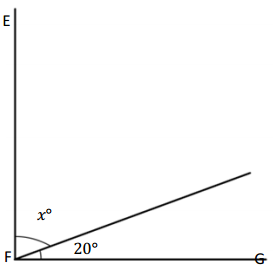
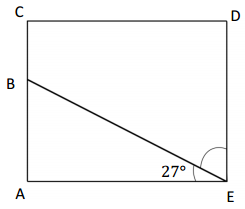
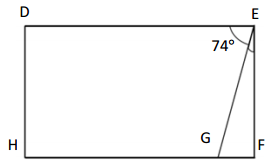
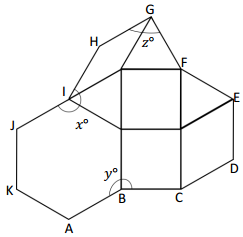
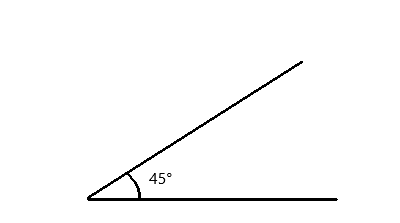
Question 1.
x° =
Answer:
The value of x° is 24°.
Explanation:
In the above image, we can see that the angle AEB is 180° and angle AEF is 90°. So the equation will be 90°+x+66= 180° and the value of m°= 180° – 156°
x°= 24°.
So the value of x° is 24°.
Question 2.
y° =
Answer:
The value of y° is 156°.
Explanation:
In the above image, we can see that the angle AEB is 180° and angle AEF is 90°. So the equation will be 24°+y= 180° and the value of y°= 180° – 24°
y°= 156°.
So the value of y° is 156°.
Question 3.
z° =
Answer:
The value of z° is 24°.
Explanation:
In the above image, we can see that the angle AEB is 180° and angle FEB is 90°. So the equation will be 90°+z+66= 180° and the value of m°= 180° – 156°
z°= 24°.
So the value of z° is 24°.
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 4 Lesson 11 Homework Answer Key
Write an equation, and solve for the unknown angle measurements numerically.
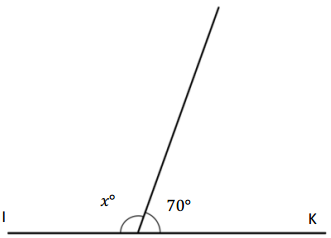
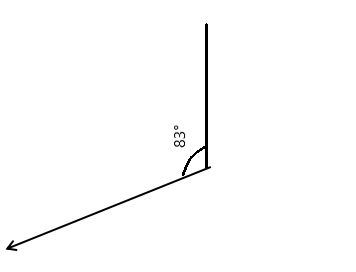
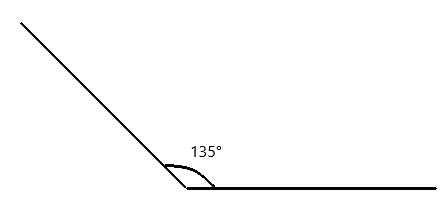
Question 1.
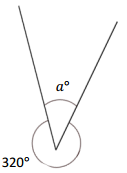
__________° + 320° = 360°
a° = ________ °
Answer:
The value of a° is 40°.
Explanation:
Given that the value of the angle is complete rotation which 360° and the value of the other angle is 320° and the value of another angle is a°. So the equation will be
a° + 320°= 360°
so the value of a° is 360° – 320°
= 40°.
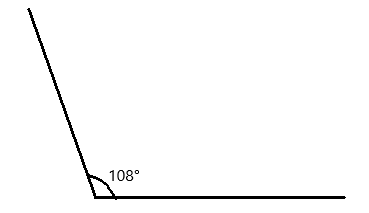
Question 2.
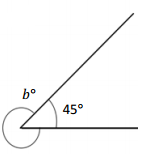
_____________ ° + ____________ ° = 360°
b° = __________ °
Answer:
The value of b° is 315°.
Explanation:
Given that the value of the angle is complete rotation which 360° and the value of the other angle is 45° and the value of another angle is b°. So the equation will be
b° + 45°= 360°
so the value of b° is 360° – 45°
=315°
Question 3.
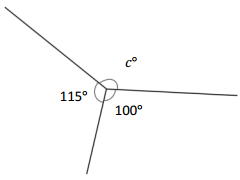
_____________ ° + _____________ ° + _____________ ° = _____________ °
c° = _____________ °
Answer:
The value of c° is 145°.
Explanation:
Given that the value of the angle is complete rotation which 360° and the value of the other angle is 115° and the value of another angle is 100° and the value of another angle is c°. So the equation will be c°+115°+100°= 360°.
c° + 215°= 360°
so the value of c° is 360° – 215°
=145°.
Question 4.
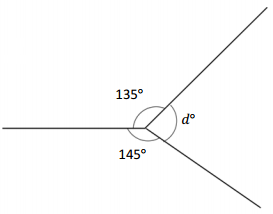
_____________ ° + _____________ ° + _____________ ° = _____________ °
d° = _____________ °
Answer:
The value of d° is 80°.
Explanation:
Given that the value of the angle is complete rotation which 360° and the value of the other angle is 135° and the value of another angle is 145° and the value of another angle is d°. So the equation will be d°+135°+145°= 360°.
d° + 280°= 360°
so the value of c° is 360° – 280°
=80°.
Write an equation, and solve for the unknown angles numerically.
Question 5.
O is the intersection of \(\overline{A B}\) and \(\overline{C D}\). ∠COB is 145°, and ∠AOC is 35°
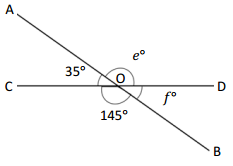
e° = _____________ ° f° = _____________ °
Answer:
The value of e° is 145°.
The value of y° is 35°.
Explanation:
In the above image, we can see that the angle COD is 180° and <COB is 145° and <AOC is 35°. So the equation will be 35° + e°= 180° and the value of e°= 180° – 35°
e°= 145°.
So the value of e° is 145°.
And the other equation will be 145° + f°= 180°
x°= 180° – 145°
= 35°.
Question 6.
O is the intersection of \(\overline{Q R}\) and \(\overline{S T}\). ∠QOS is 55°
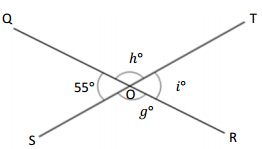
g° = _____________ ° h° = _____________ ° i° = _____________ °
Answer:
The value of g° is 125°.
The value of h° is 125°.
The value of i° is 55°.
Explanation:
In the above image, we can see that the angle SOT is 180° and angle QOR is 180° and <QOS is 55°. So the equation will be 55° + g°= 180° and the value of g°= 180° – 55°
g°= 125°.
So the value of g° is 125°.
And the other equation will be 55° + h°= 180°
h°= 180° – 55°
= 125°.
So the value of the h°is 125°.
And the other equation will be 125° +g°= 180°
g°= 180° – 125°
= 55°.
So the value of the g°is 55°.
Question 7.
O is the intersection of \(\overline{U V}\), \(\overline{W X}\), and \(\overline{Y O}\). ∠VOX is 46°
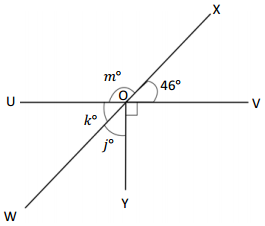
J° = _____________ ° K° = _____________ ° m° = _____________ °
Answer:
The value of j° is 44°.
The value of k° is 46°.
The value of m° is 134°.
Explanation:
In the above image, we can see that the angle WOX is 180° and angle UOV is 180° and <VOX is 46°. So the equation will be 46° +90°+ j°= 180° and the value of j°= 180° – 136°
j°= 44°.
So the value of j° is 44°.
And the other equation will be 44° +90°+ k°= 180°
k°= 180° – 134°
= 46°.
So the value of the k°is 46°.
And the other equation will be 46° +m°= 180°
m°= 180° – 46°
= 134°.
So the value of the m°is 134°.