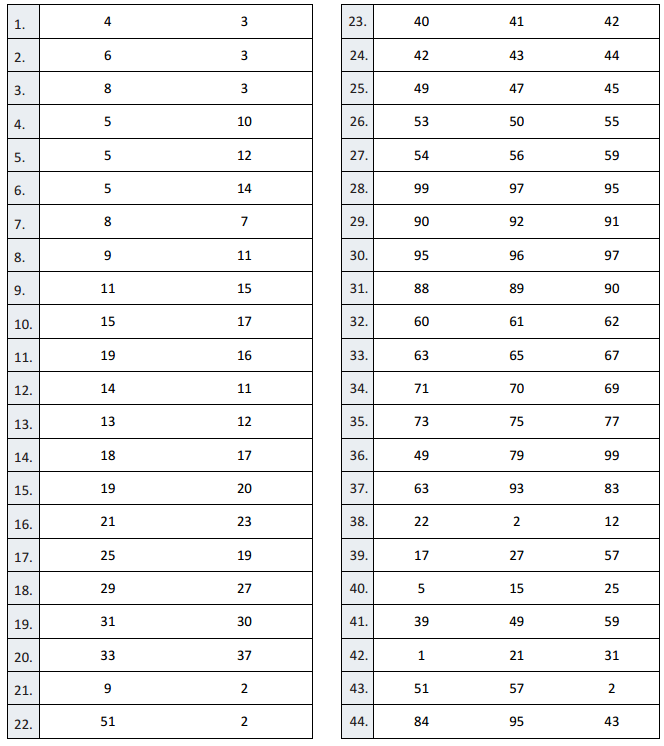
Engage NY Eureka Math 4th Grade Module 3 Lesson 29 Answer Key
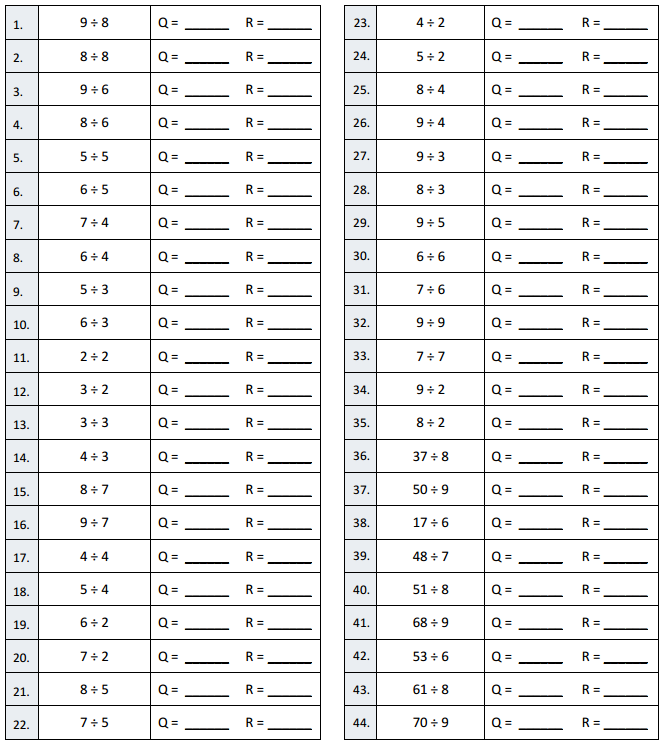
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 3 Lesson 29 Problem Set Answer Key
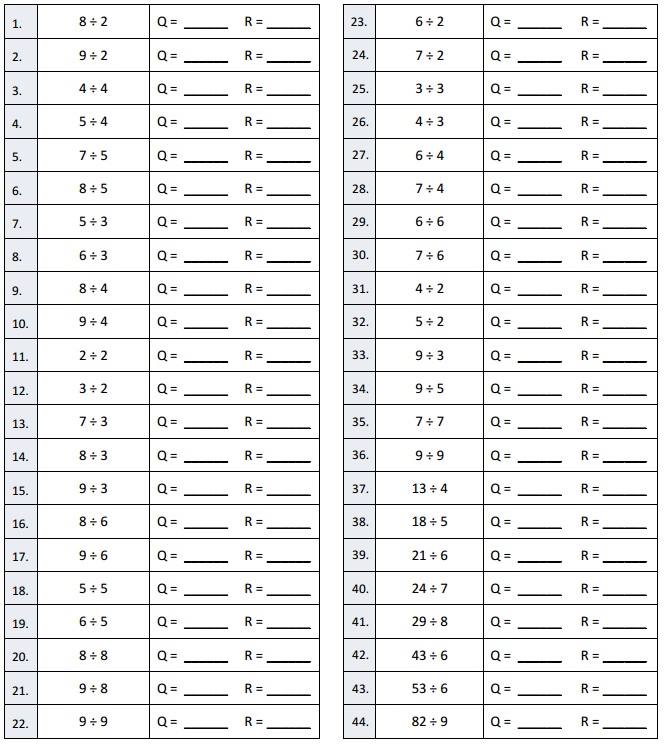
Question 1.
Divide, and then check using multiplication.
a. 1,672 ÷ 4
Answer:
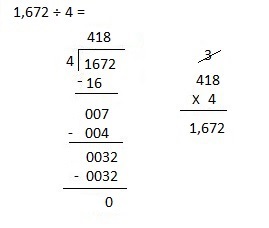
Explanation:
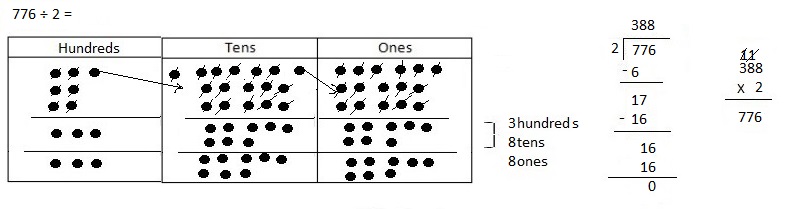
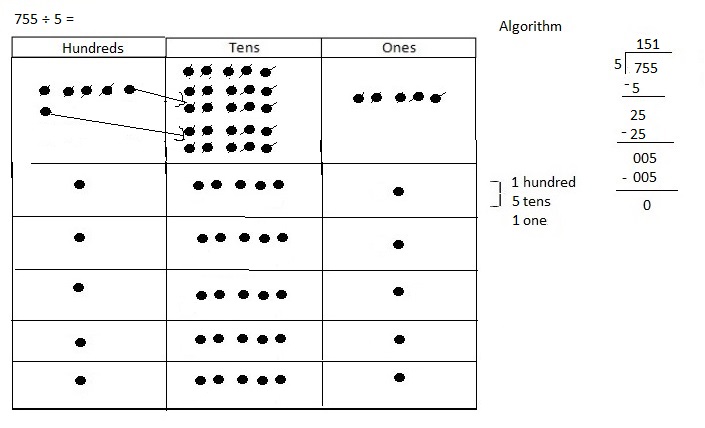
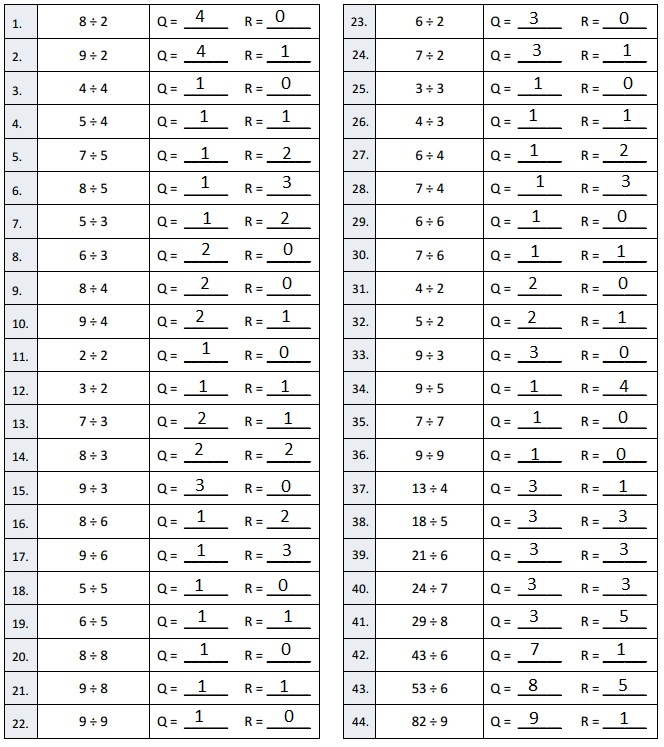
Divided 1,672 ÷ 4 = 418 and then checked using multiplication
418 X 4 = 1,672.
b. 1,578 ÷ 4
Answer:
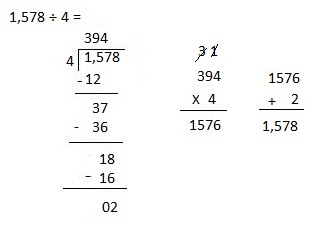
Explanation:
Divided 1,578 ÷ 4 = 394, Remainder 2 and then checked using multiplication and adding 2 as
394 X 4 = 1,576, 1,576 + 2 = 1,578.
c. 6,948 ÷ 2
Answer:
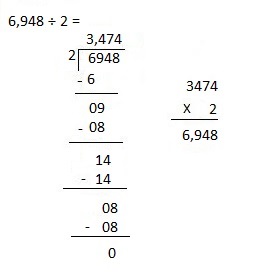
Explanation:
Divided 6,948 ÷ 2 = 3,474 and then checked using
multiplication as 3,474 X 2 = 6,948.
d. 8,949 ÷ 4
Answer:
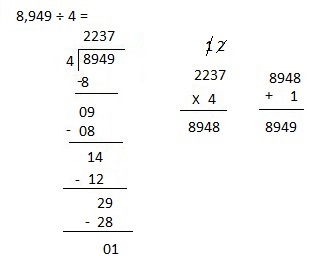
Explanation:
Divided 8,949 ÷ 4 = 2,237, Remainder 1 and then checked using
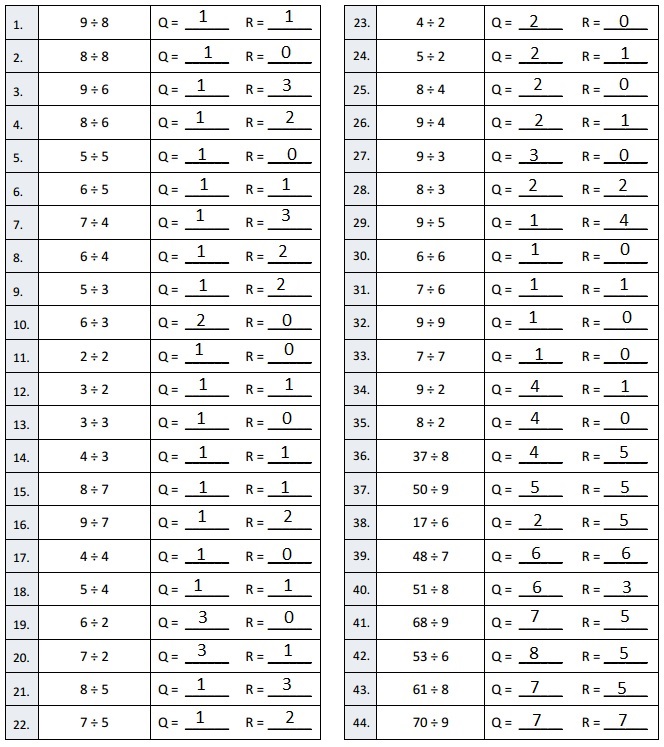
multiplication and adding 1 as 2,237 X 4 = 8,948,
8,948+ 1 = 8,949.
e. 7,569 ÷ 2
Answer:
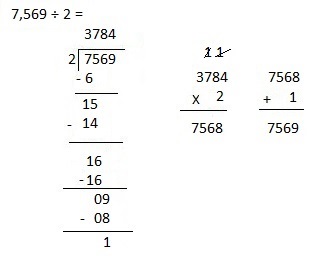
Explanation:
Divided 7,569 ÷ 2 = 3,784, Remainder 1 and then checked using multiplication and adding 1 as
3,784 X 2 = 7,568, 7,568 + 1 = 7,569.
f. 7,569 ÷ 3
Answer:
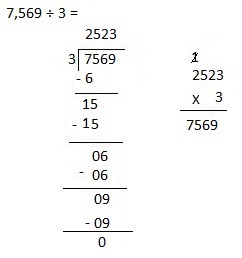
Explanation:
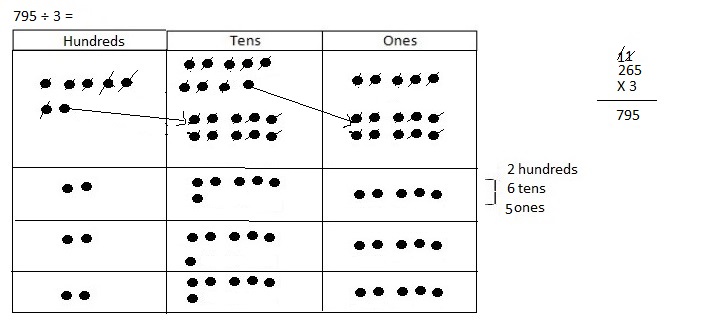
Divided 7,569 ÷ 3 = 2,523 and then checked using multiplication as 2,523 X 3 = 7,569.
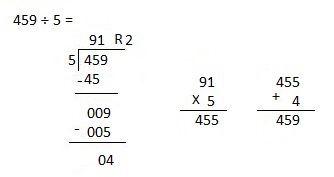
g. 7,955 ÷ 5
Answer:
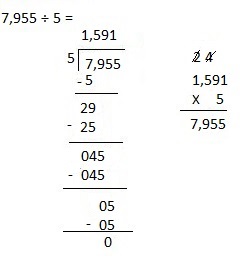
Explanation:
Divided 7,955 ÷ 5 = 1,591 and then checked using multiplication as 1,591 X 5 = 7,955.
h. 7,574 ÷ 5
Answer:
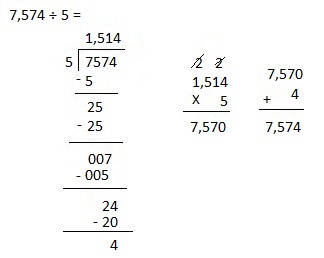
Explanation:
Divided 7,574 ÷ 5 = 1,514, Remainder 4 and then checked using multiplication and adding 4 as 1,514 X 4 = 7,570, 7,570 + 4 = 7,574.
i. 7,469 ÷ 3
Answer:
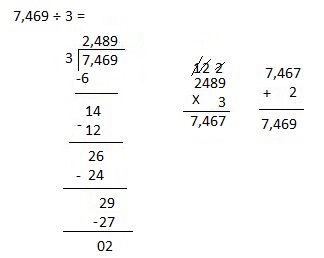
Explanation:
Divided 7,469 ÷ 3 = 2,489, Remainder 2 and then checked using multiplication and adding 2 as 2,489 X 2 = 7,467, 7,467 + 2 = 7,469.
j. 9,956 ÷ 4
Answer:
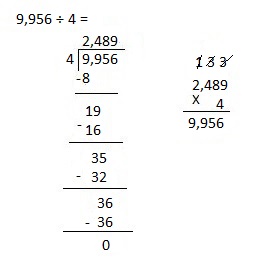
Explanation:
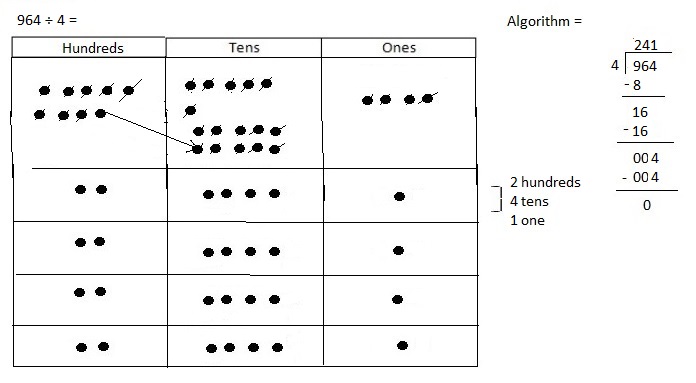
Divided 9,956 ÷ 4 = 2,489 and then checked using multiplication as 2,489 X 4 = 9,956.
Question 2.
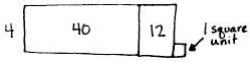
There are twice as many cows as goats on a farm. All the cows and goats have a total of 1,116 legs. How many goats are there?
Answer:
There are 93 goats,
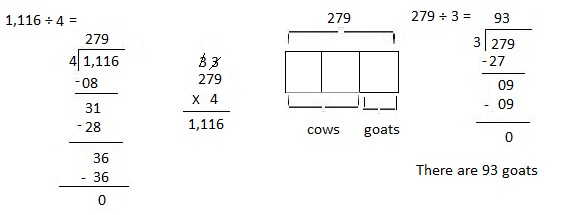
Explanation:
Given there are twice as many cows as goats on a farm.
All the cows and goats have a total of 1,116 legs.
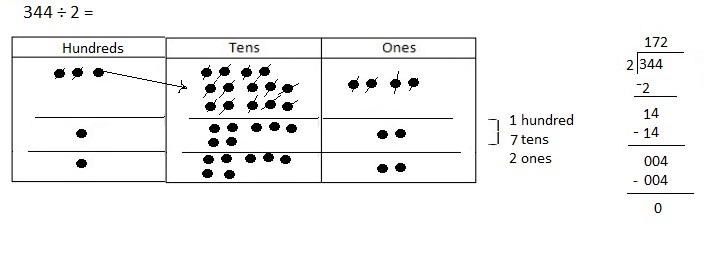
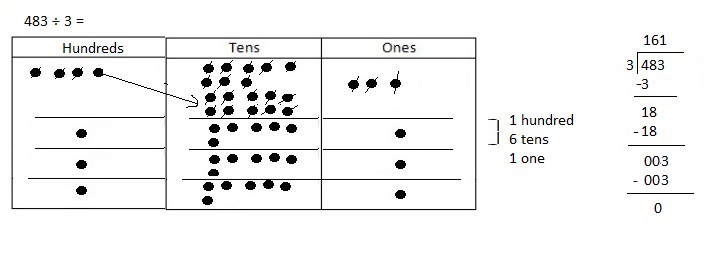
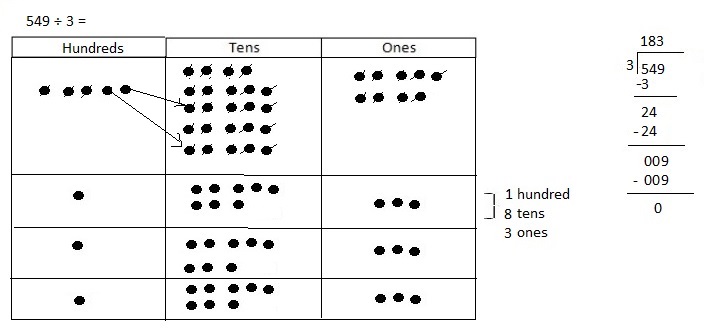
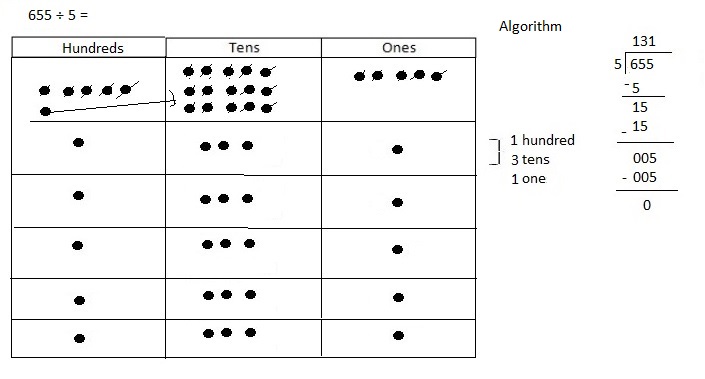
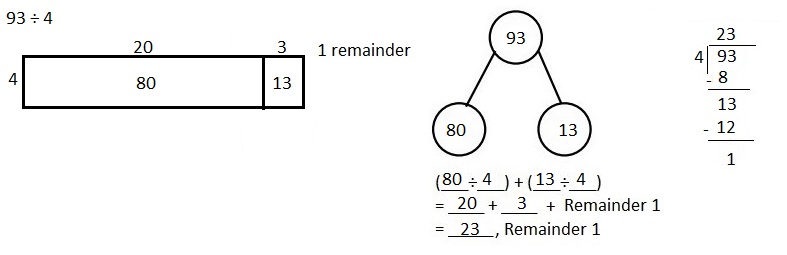
Number of cows and goats are 1,116 ÷ 4 = 279,
So number of goats are 279 ÷ 3 = 93 as shown above.
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 3 Lesson 29 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Question 1.
Divide, and then check using multiplication.
a. 1,773 ÷ 3
Answer:
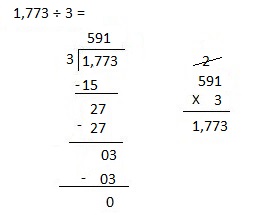
Explanation:
Divided 1,773 ÷ 3 = 591 and then checked using multiplication as 591 X 3 = 1,773.
b. 8,472 ÷ 5
Answer:
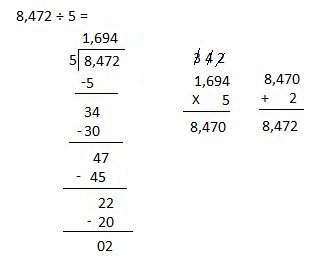
Explanation:
Divided 8,472 ÷ 5 = 1,694, Remainder 2 and then checked using multiplication and adding 2 as 1,694 X 5 = 8,470, 8,470 + 2 = 8,472.
Question 2.
The post office had an equal number of each of 4 types of stamps. There was a total of 1,784 stamps. How many of each type of stamp did the post office have?
Answer:
Each type of stamp did the post office have is 446,
Explantion:
Given the post office had an equal number of each of 4 types of stamps.
There was a total of 1,784 stamps.
So number of each type of stamp did the post office have is
1,784 ÷ 4 =
446
4|1,784
16
18
16
24
24
0
Therefore, number of each type of stamp did the post office have is 446.
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 3 Lesson 29 Homework Answer Key
Question 1.
Divide, and then check using multiplication.
a. 2,464 ÷ 4
Answer:
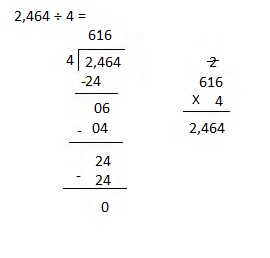
Explanation:
Divided 2,464 ÷ 4 = 616 and then checked using multiplication as 616 X 4 = 2,464.
b. 1,848 ÷ 3
Answer:
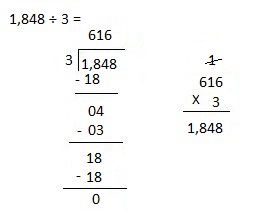
Explanation:
Divided 1,848 ÷ 3 = 616 and then checked using multiplication as 616 X 3 = 1,848.
c. 9,426 ÷ 3
Answer:
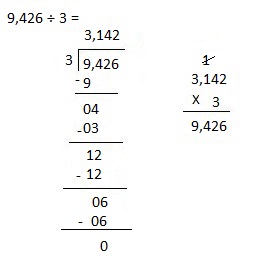
Explanation:
Divided 9,426 ÷ 3 = 3,142 and then checked using multiplication as 3,142 X 3 = 9,426.
d. 6,587 ÷ 2
Answer:
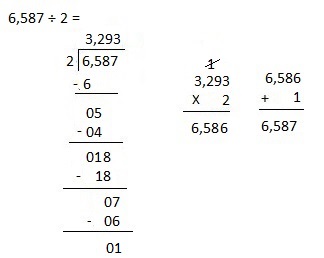
Explanation:
Divided 6,587 ÷ 2 = 3,293, Remainder 1 and then checked using multiplication and adding 1 as 3,293 X 2 = 6,586, 6,586 + 1 = 6,587.
e. 5,445 ÷ 3
Answer:
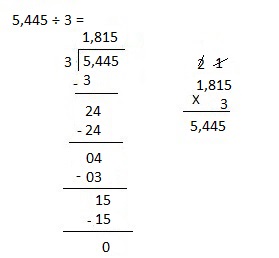
Explanation:
Divided 5,445 ÷ 3 = 1,815 and then checked using multiplication as 1,815 X 3 = 5,445.
f. 5,425 ÷ 2
Answer:
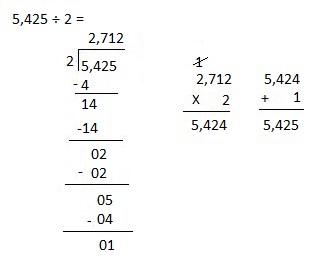
Explanation:
Divided 5,425 ÷ 2 = 2,712, Remainder 1 and then checked using multiplication and adding 1 as 2,712 X 2 = 5,424, 5,424 + 1 = 5,425.
g. 8,467 ÷ 3
Answer:
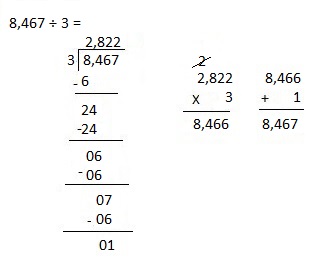
Explanation:
Divided 8,467 ÷ 3 = 2,822, Remainder 1 and then checked using multiplication and adding 1 as 2,822 X 3 = 8,466, 8,466 + 1 = 8,467.
h. 8,456 ÷ 3
Answer:
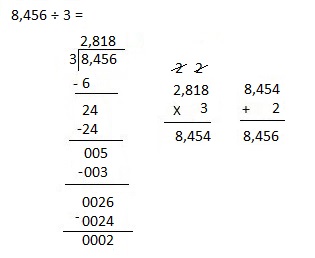
Explanation:
Divided 8,456 ÷ 3 = 2,818, Remainder 2 and then checked using multiplication and adding 2 as 2,818 X 3 = 8,454, 8,454 + 2 = 8,456.
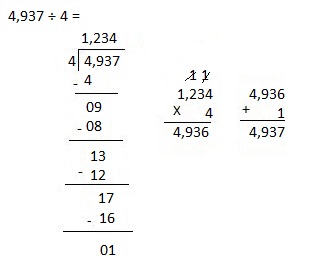
i. 4,937 ÷ 4
Answer:
Explanation:
Divided 4,937 ÷ 4 = 1,234, Remainder 1 and then checked using multiplication and adding 1 as 1,234 X 4 = 4,936, 4,936 + 1 = 4,937.
j. 6,173 ÷ 5
Answer:
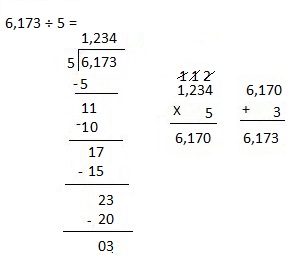
Explanation:
Divided 6,173 ÷ 5 = 1,234, Remainder 3 and then checked using multiplication and adding 3 as 1,234 X 5 = 6,170, 6,170 + 3 = 6,173.
Question 2.
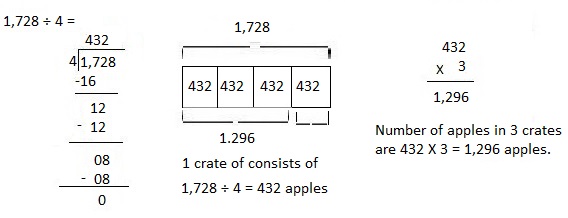
A truck has 4 crates of apples. Each crate has an equal number of apples. Altogether, the truck is carrying 1,728 apples. How many apples are in 3 crates?
Answer:
1,296 apples are there in 3 crates,
Explanation:
Given a truck has 4 crates of apples. Each crate has an equal number of apples.
Altogether, the truck is carrying 1,728 apples.
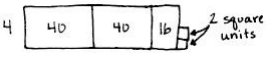
So, 1 crate of consists of 1,728 ÷ 4 = 432 apples
Therefore number of apples in 3 crates are 432 X 3 = 1,296 apples.
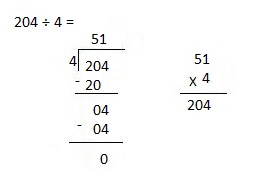
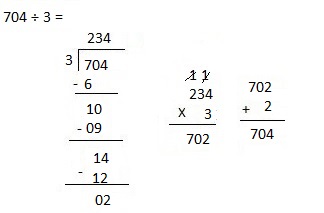
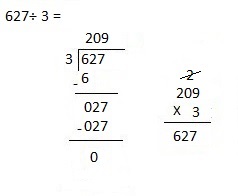
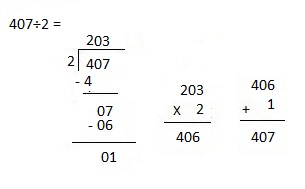
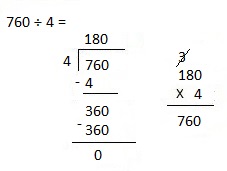
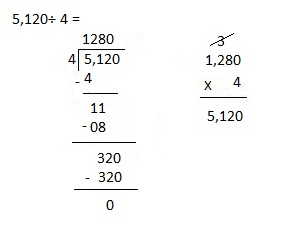

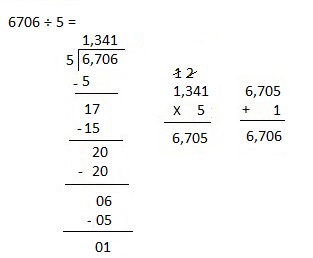
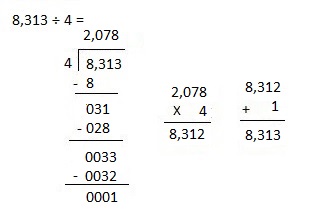
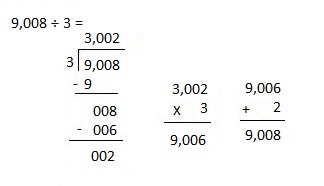
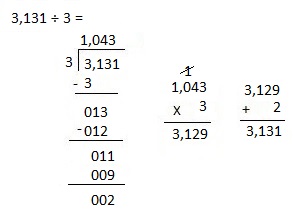
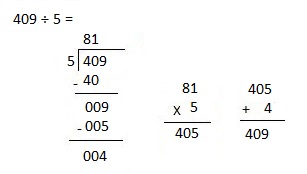
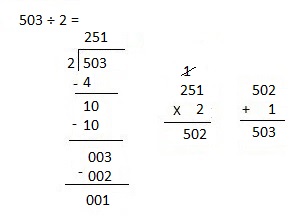
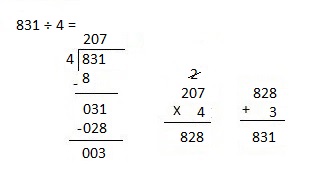
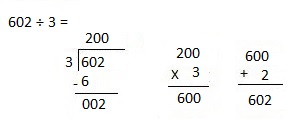
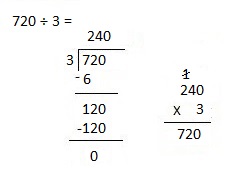
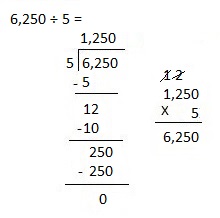
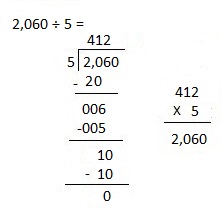
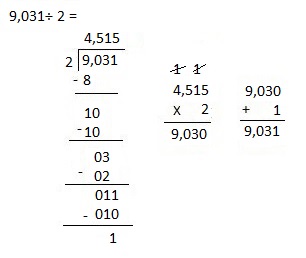
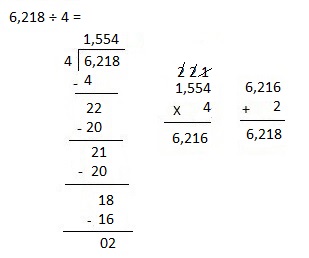
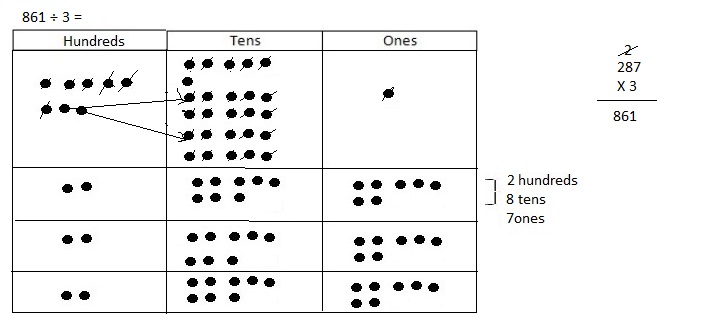
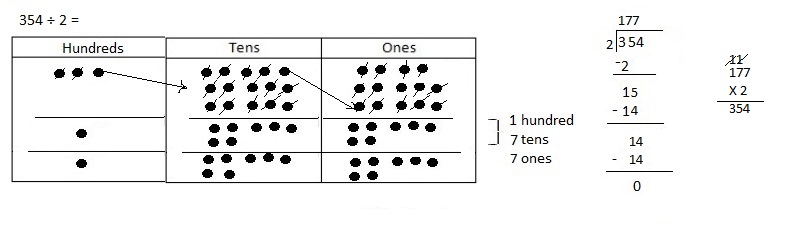
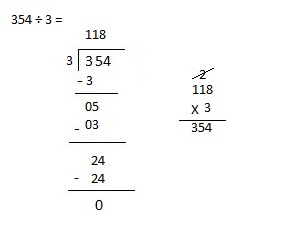
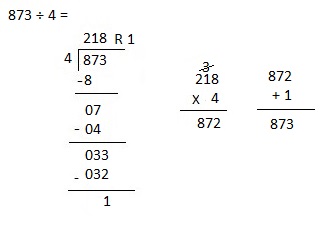

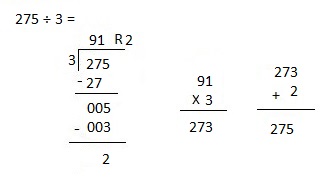
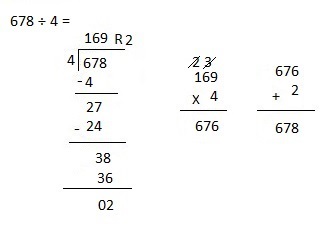
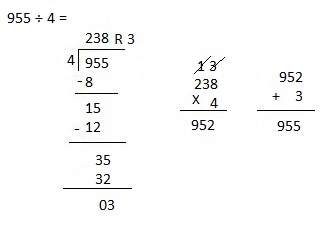
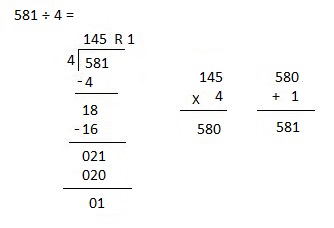
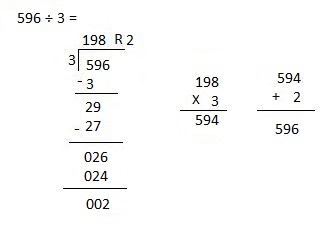
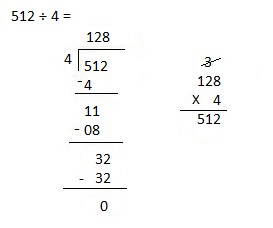
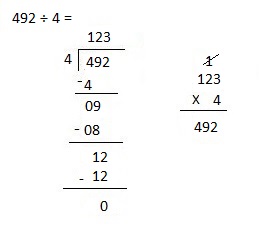
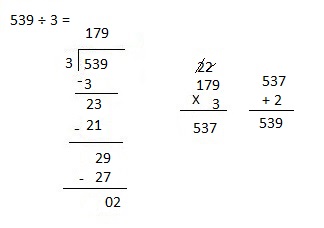
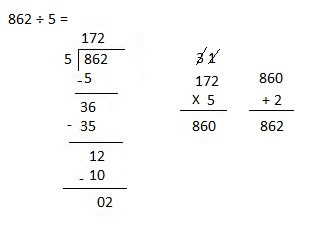
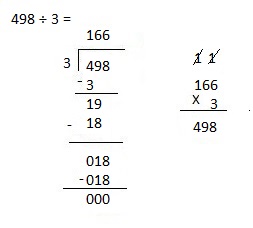
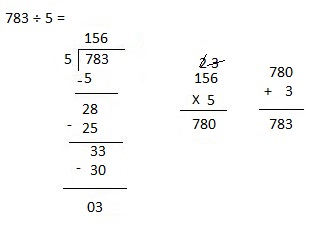
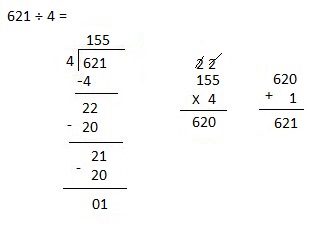
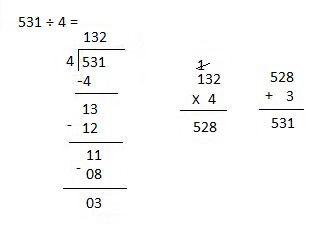
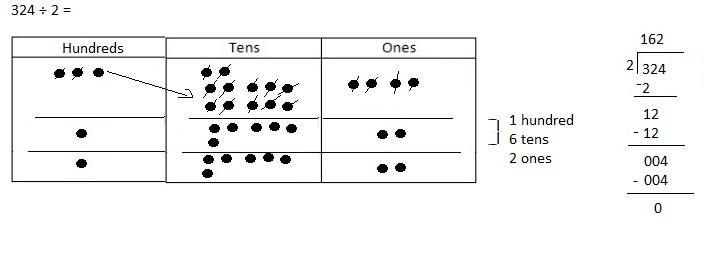
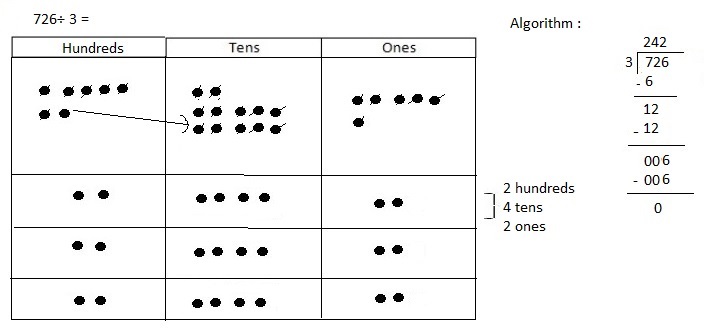
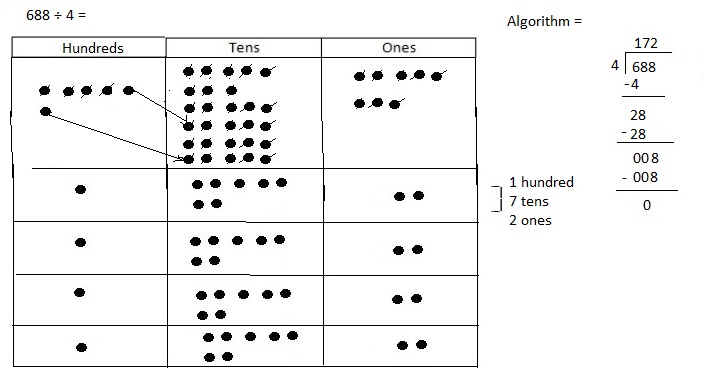

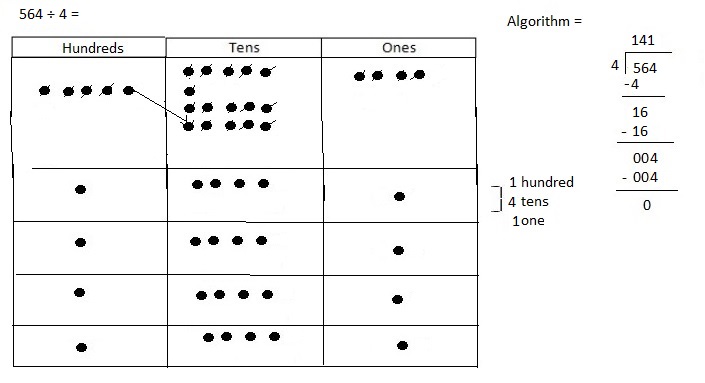
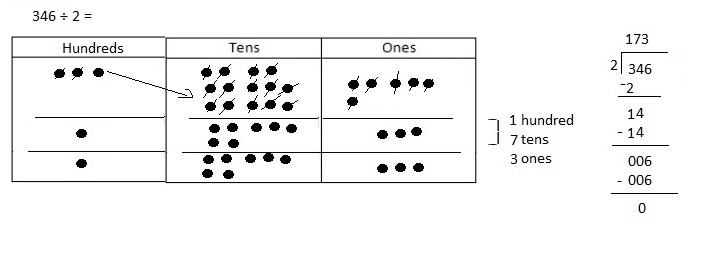
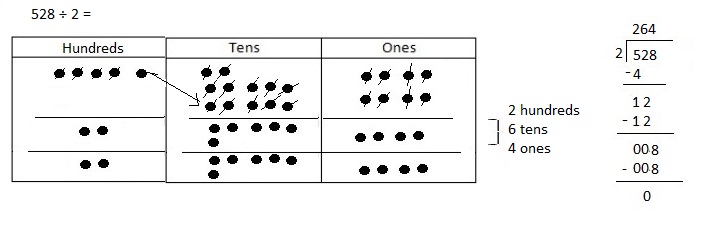
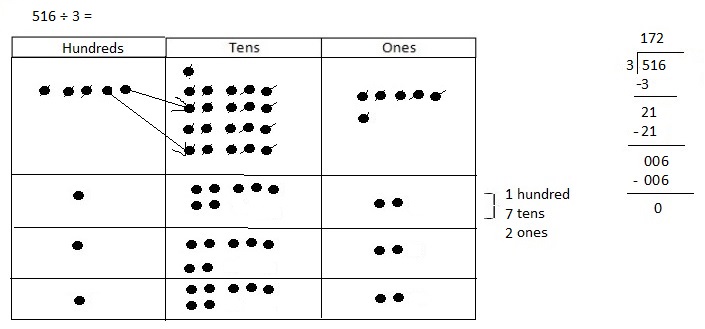
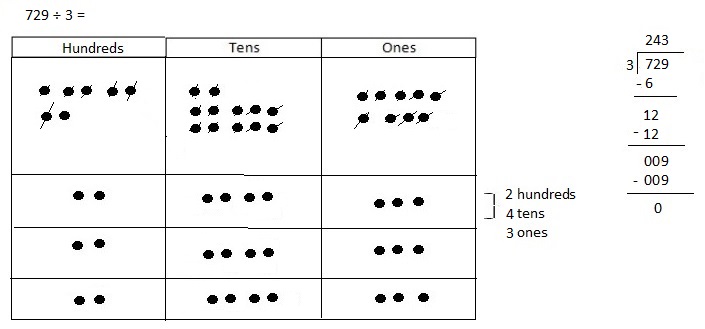
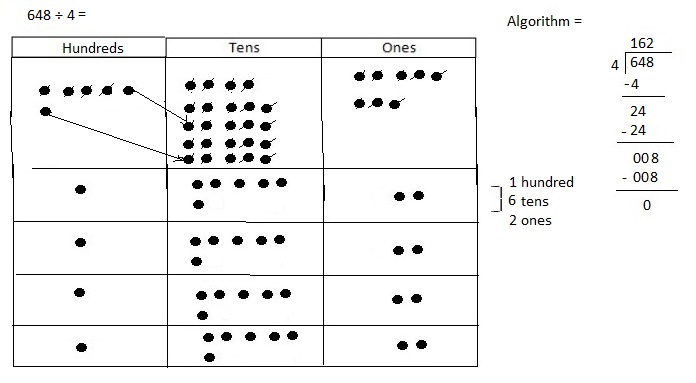

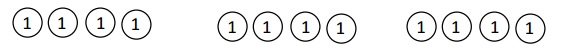
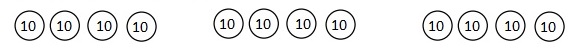
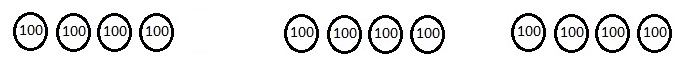
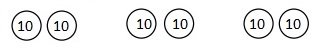
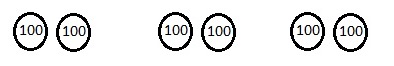
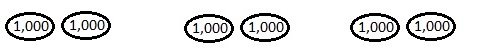

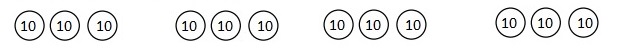
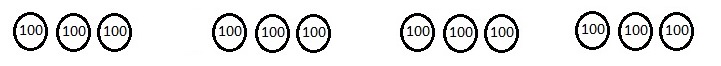
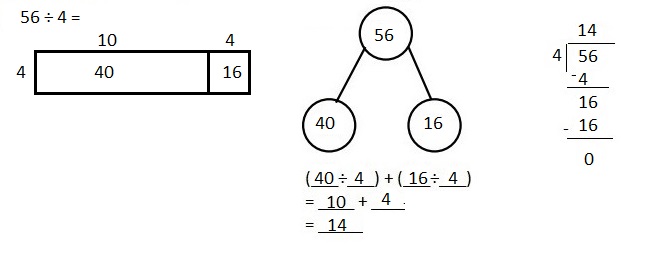
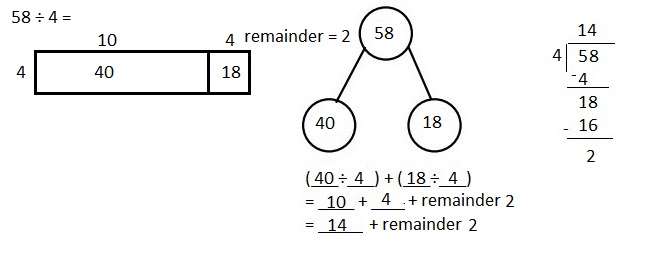
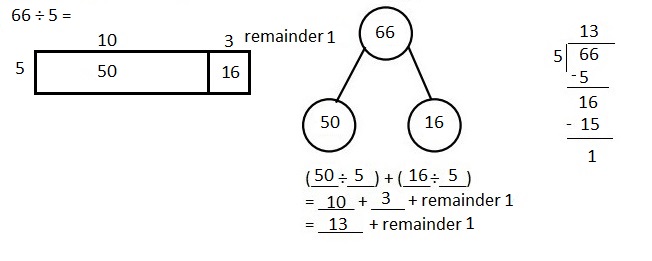
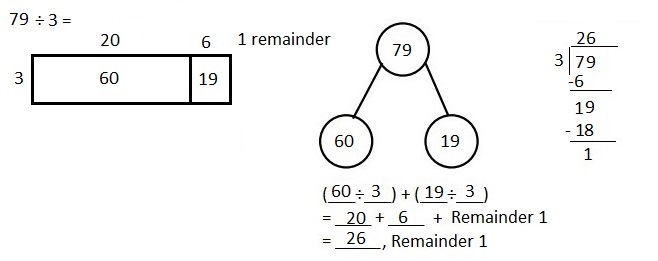
 Explanation:
Explanation:
 Explanation:
Explanation: